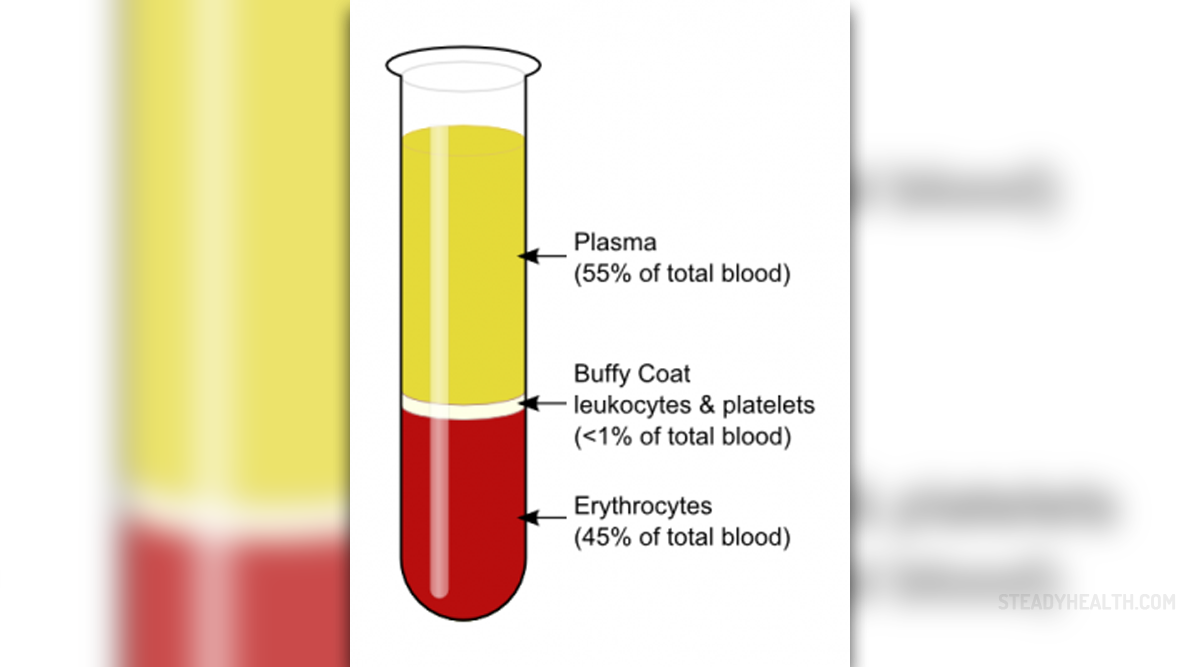
The presence of red blood cells in the urine is medically known as the hematuria or haematuria. For most of the patients this is the most unusual and worrying sign that something isn't right with one’s health.
However, no matter how strange it may look like, blood in urine isn’t always a matter for concern. Sometimes the blood enters the urine as a side-effect of vigorous exercise or because of the use of certain prescribed medicines, Aspirin for example. However, sometimes it may be caused by some other serious health disorder.
Types of blood in urine
Blood in urine may sometimes be obvious while sometimes doctors need to use a microscope to determine if there is a blood in urine. Normally visible blood is called “gross hematuria” while the blood visible only under the microscope is called “microscopic hematuria”. Presence of the blood in urine that may be noticed with the naked eyes indicates heavily increased secretion of the blood. The urine may even change color, turning red, brown or pink. In some cases, blood clots may also be present. Increased concentration of blood in urine may indicate serious underlying cause and possible life threatening conditions, so it demands immediate medical care.
Causes of blood in urine
Blood in urine usually indicates urinary tract infection or other health problems. Normally, kidneys are processing blood, removing the waste and excessive fluids and converting the fluid into the urine. From the kidneys, urine flows through ureters to the bladder. Any kind of disturbance in the is process may cause blood cells to leak into the urine.
Most commonly, urinary tract infections are causing the blood in urine. The infections develop when the bacteria enter the body through the urethra and form a colony inside the bladder. Symptoms of urinary tract infections include pain and burning during urination or increased urge to urinate.
Kidney infections may also cause red urine. These infections occur when a bacteria move up from the ureters to kidneys or gets into the kidneys trough the bloodstream, causing the similar symptoms as the bladder infection.
A bladder or kidney stone may sometimes cause a blockage or cause a sharp pain as they are being passed. These small hard stones may form micro-abrasions on the walls of the kidneys or bladder, causing gross or microscopic bleeding.
Enlargement of the prostate gland may sometimes compress the urethra and block the flow of urine. Patients with this problem may complain about difficulty to urinate and an increased urge to urinate. Gross or microscopic blood may also be present in their urine.
Visible blood in the urine may sometimes indicate the presence of advanced kidney, bladder or prostate cancer.
















Your thoughts on this
Loading...