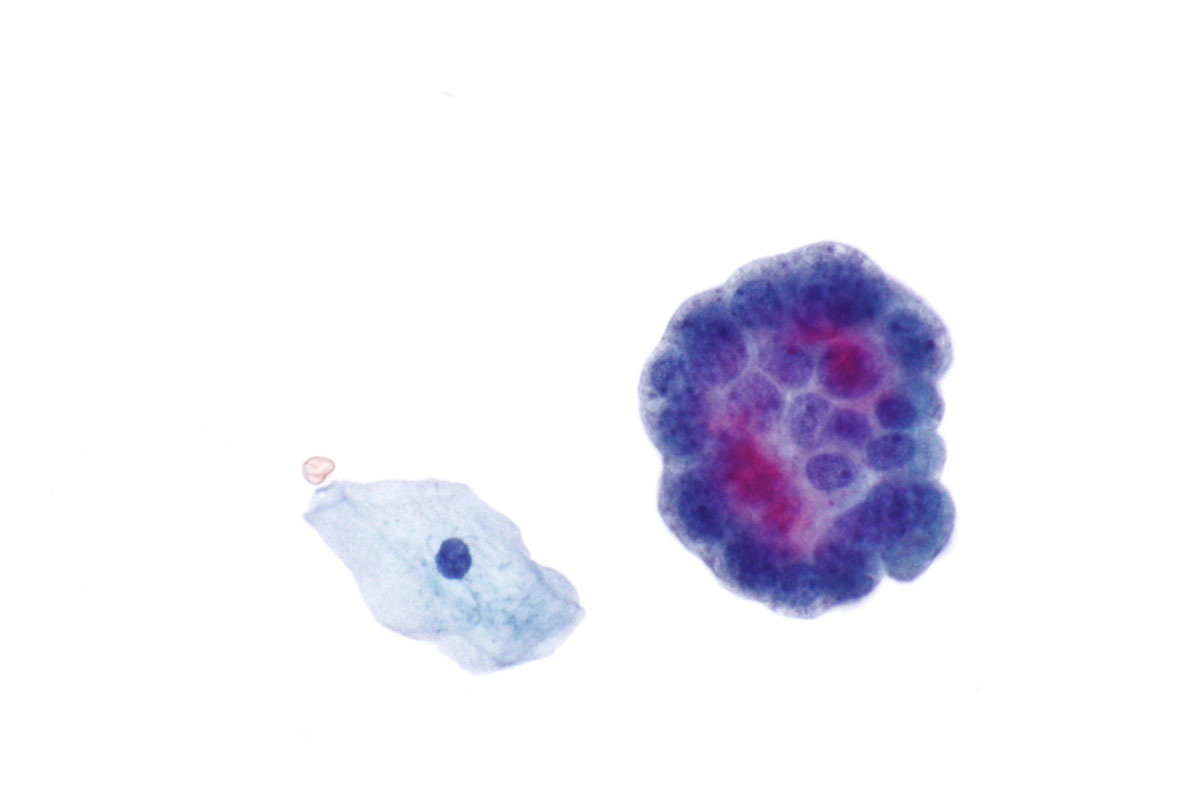
Blood in Urine - Hematuria
Blood in urine - hematuria is a common symptom that sometimes even doesn’t requires treatment but sometimes may be a symptom of a serious health problem. The presence of blood in the urine is not always obvious. When the amount of the red blood cells in urine is small it looks normal. This is called microscopic hematuria as erythrocytes are visible only under a microscope. It usually discovers during the urine test for some other reason. When blood is visible in the urine, it may look pinkish, dark brown (like tea) or red. A very small amount of blood in the urine is necessary to be visible - about one fifth of teaspoons of blood to the half-liter of urine. Traces of blood in the urine are normal phenomenon. Healthy people with healthy urinary tract excrete about 1 million red cells through the urine per day. This amount of blood is not visible and is not considered as hematuria.Large amounts of blood in the urine can be acute (occur suddenly) or chronic (last for a long time). More than 10% of people have hematuria and 3% develop intense hematuria.
Causes of Hematuria
Blood in the urine may appear due to any disease that is a result of infection, inflammation or injured urinary tract.Usually, microscopic hematuria indicates the damage of the upper parts of the urinary tract - the kidneys, while visible blood in the urine indicates damage the lower urinary tract parts - ureter, bladder and urethra.
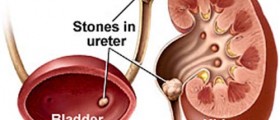
The most frequent cause in young people under the 40 is the kidney stone or the ureter and urinary tract infections. These also may cause hematuria in people over the age of 40 but then cause of hematuria is more likely kidney, bladder and prostate cancer. Sometimes hematuria is the result of several causes of which some are harmless but some aren’t.
A well-known causes of hematuria are: kidney stone, urinary tract or genital organs (often in women) infections, tumor and tissue pressure around urethra and its blockade by stone kidney, bladder or prostate cancer, diseases and inflammations of the kidneys, blood pressure disorders, injuries, some medicines such as antibiotic - rifampin, analgesics - Aspirin, anticoagulants –warfarin and some laxatives, benign prostate enlargement in older men, chronic diseases like diabetes, hypertension and anemia, viral infectionssome food such as beets, blueberries, rhubarb and colors for cakes liver disease. Also, urine may be pink, red or dark brown due to reason which isn’t related to bleeding in the urinary tract.














Your thoughts on this
Loading...