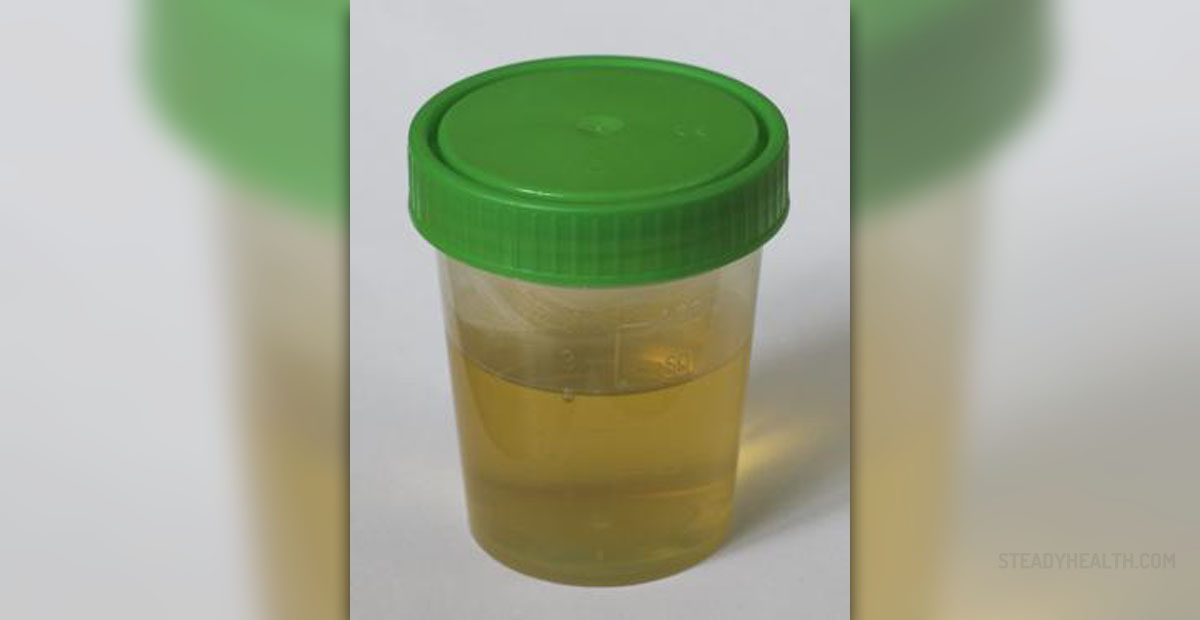

Urinating blood - hematuria
Urinating blood is clinically called hematuria and is among the most frightening conditions since the person becomes terrified when he/she notices blood in the urine, fearing of the presence of some life threatening condition. Hematuria may be divided into two types - microscopic hematuria and gross hematuria, and while microscopic hematuria is marked by the presence of very small quantities of blood in urine, which can only be seen by the means of a microscope, gross hematuria is a condition in which the blood in urine can be perceived with the naked eye. In women, the blood in urine comes from the vagina, while in the men it comes from the affected prostate.Causes of urinating bloodWhen the kidneys and bladder develop cancer, it may be manifested through the urinating blood and those people with any of these two cancer types often experience hematuria, especially microscopic hematuria.
Furthermore, urinating blood may be caused by the bladder stones, which are the crystalline masses made of protein and minerals, and which may be formed in any place in the urinary tract before they reach the bladder. In the beginning, these stones are very tiny but they gradually become larger, causing eventually the blockage of the normal urinal flow. The bladder stones may sometimes scratch the bladder wall, causing the infection or bleeding in the bladder and subsequently the blood in the urine.
Acute and chronic kidney failure are also among the possible causes for the occurrence of hematuria. Acute renal failure is when one experiences sudden loss of functionalities of his/her kidneys. On the other side, chronic renal failure develops gradually over time, when the kidneys slowly lose their capability to filter the blood and to assist in the process of excretion of the waste products. Apart from hematuria, acute and chronic kidney failures are manifested through the frequent, problematic and painful urination.
Urinating blood is a disorder that usually occurs in people who develop the condition called glomerulonephritis, which occurs due to damage of the kidney part responsible for filtering of the blood. Glomerulonephritis is primary when it develops alone, while secondary glomerulonephritis develops out of some other ailment, such as diabetes and lupus, for instance. Hematuria, hypertension, less frequent urination and diluted and foamy urine are the most common signs of this condition.
As we can see, blood in urine is a symptom that indicates some serious disease, and therefore, it should be taken seriously. There are also some other causes for the incidence of the bloody urine but these are the most serious.
- www.nhs.uk/conditions/blood-in-urine/
- medlineplus.gov/ency/article/003138.htm
- Photo courtesy of Polarlys by Wikimedia Commons: commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:Urinbecher.jpg















Your thoughts on this
Loading...