Types of Burns
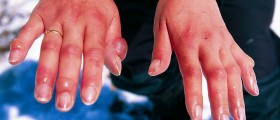
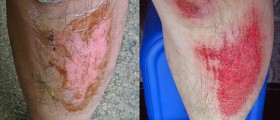
Not every burn is the same. Burns can be thermal, electrical and chemical. Different types of burns need to be treated differently. When it comes to chemical burns, classic remedies are not very efficient. Electrical burns are easily treated with the hydration process and thermal with analgesics and topical antibiotics. It is recommendable that you report any allergies that you may have regarding medications before the doctor suggests the treatment for your burn.
For thermal burns, the most efficient medications are topical antibiotics, Silvadene, analgesics, nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory agents and the procedure called dermabrasion. Topical antibiotics like Neosporin and Silvadene are used to fight infections and bacteria growth. They should be dosed around the clock, 1 to 3 times per day. Neosporin is easy to find in drug stores and you don’t need a prescription to buy it. Silvadene is used for severe burns and requires a prescription and a sterile application environment.
Most common analgesics that are used to reduce pain followed by thermal burns are morphine sulfate, vicodin and Demerol. They all must be prescribed by a doctor. Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory agents are often used instead of steroids to help treat mild to moderate pain. They include ibuprofen, Ansaid and Anaprox.
- Insulin decreases blood glucose because it mediates peripheral glucose uptake into skeletal muscle and adipose tissue, and also suppresses hepatic gluconeogenesis.
- Anabolic steroids such as oxandrolone (a testosterone analog which possesses only 5% of the undesirable androgenic effects of testosterone) are beneficial for muscle protein catabolism because they enhance protein synthesis, reduce weight loss, and improve the healing of skin graft donor sites. In a prospective randomized study, administration of 10 mg of oxandrolone every 12 h decreased the hospital stay. However, it is important to monitor hepatic transaminases to avoid liver toxicity.
- The antidiabetic biguanide drug, metformin (Glucophage) is used to inhibit gluconeogenesis in the liver, and increase peripheral insulin sensitivity by stimulating glucose transporters. In 10 patients with >60% TBSA burns, metformin attenuated hyperglycemia, and led to a significantly lower rate of endogenous glucose production and glucose oxidation.
- Adrenergic blockade (the administration of beta blockers) has effects on metabolism besides the well-known effects on blood pressure and heart rate. In 406 children with >30% TBSA burns propranolol treatment reduced thermogenesis, heart rate, and resting energy expenditure.
- Glucagon like peptide 1 (GLP1) is an incretin, which is secreted into the hepatic portal system (by the intestinal L-cells) after a meal, thus enhancing the secretion of insulin. An infusion of GLP1 by osmotic pump was tested in rats with 40% TBSA burns.
- Although corticosteroids are the classical anti-inflammatory agents, their use is controversial in burn wound healing. Singer et al showed that the topical application of a high potency topical steroid cream (clobetasol propionate) to pigs with 2nd degree burns was not able to prevent secondary burn wound progression.
Dermabrasion is a procedure that usually doesn’t require hospitalization. Different types of anesthesia can be used in this procedure: numbing spray, local anesthesia and anxiolytic. Topical antibiotics, calcium and magnesium salts give the best results in chemical burn treatment. Pain relievers like Morphine and Acetaminophen can help in reducing pain caused by burns and especially with individuals whose eyes are affected by burns. Advil, Motrin Ansaid, Naprosyn and Anaprox can also be effective in reducing the pain and they are nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory agents.
Antibiotics
Antibiotics like Silvadene are used to treat chemical burns of the second and third degree. Chemical burns commonly occur to the eyes, and erythromycin ointment is used instead of Silvadene to fight infections in the ocular area. Electrical burns are treated with medicines such as Lactated ringers and osmotic diuretics.
In treating the scars developed by burns, the usage of different gels is helpful. The most common medicines that are used are Cica-Care gel sheets and Mederma gel. Cica-Care silicone gel is a form of the treatment for thick scars. With daily use, the scar will become flatter and smoother. Mederma is a gel you apply to the skin. It contains ingredients designed to soften a scar, which can make it less noticeable. Mederma should be applied 3 to 4 times per day. Mederma treatment lasts from three to six months.











Your thoughts on this
Loading...