The abnormal growth of the cells may appear at any place in the body including our digestive system. Apart from the liver and gallbladder, the bile ducts that connect these two organs may also be affected by this abnormal cell growth. The tumors of the bile ducts are a very rare condition, but when they appear, they represent a serious problem. These tumors are very small so that even common imaging studies like ultrasonography and CT scanning are not able to detect them sometimes. Magnetic resonance cholangiography, as well as endoscopic approach, are necessary for defining the anatomy of the bile ducts and the extent of the biliary obstruction.
The bile duct tumors are very rare and it is estimate that they make up 2% of all diagnosed cancers. Benign bile duct tumors are considerably rare conditions as compared to the malign bile duct tumors. It is also observed that the benign adenomas or papillomas tend to recur once they are removed in a surgery, and that they tend to become malignant over time. The main symptom of the benign bile duct tumors is jaundice, but the occult gastrointestinal hemorrhage may also happen.
Etiology of Benign Bile Duct Tumors
There are people with certain conditions who are at higher risk to develop the bile duct tumors. The people who suffer from congenital hepatic fibrosis and Caroli disease, as well as from Von Meyenburg complexes, are more prone to develop benign bile duct tumors. Furthermore, the people with polycystic liver, choledochal cysts, gallstones and hepatolithiasis are also considered to be at high risk to experience the benign bile duct tumor symptoms.
It is also observed that the people who suffer from primary sclerosing cholangitis and those who suffer from ulcerative colitis are also prone to develop the tumor in question. Some other potential triggers for the occurrence of bile duct tumors are certain drugs, birth control pills, toxins and carcinogens like arsenic and dioxin.
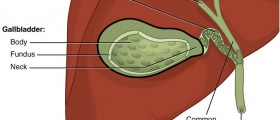
- Specific risk factors for the development of hepatobiliary cancer have been associated with different parts of the biliary tree. Gallbladder cancer is more frequent in patients with gallstones, especially if the gallstones are symptomatic and large. Other factors associated with gallbladder cancer include female sex, obesity, and high carbohydrate intake, all of which are also associated with gallstone disease.
- Adenomas of the ampulla of Vater, especially when they are villous, are known to be premalignant lesions. Adenomas are frequently seen in patients with familial adenomatous polyposis, who have a risk of ampullary adenocarcinoma that is 100 times that in the normal population.
- Patients who have ulcerative colitis in the absence of symptomatic primary sclerosing cholangitis or who have long-standing intraductal gallstone disease also have an increased risk. Other, rarer conditions associated with the development of cholangiocarcinoma include bile-duct adenoma, multiple biliary papillomatosis, choledochal cysts, Caroli's disease (cystic dilatation of intrahepatic bile ducts), and exposure to the radiopaque medium thorium dioxide (Thorotrast).
Symptoms of Benign Bile Duct Tumors
In most cases, the benign bile duct tumors occur in the elderly population, particularly people above 60 years of age. When one develops this bile duct disorder, the first sign is jaundice, which is usually followed by pruritis. However, if only one bile duct is affected, the jaundice may be delayed since the liver can compensate.
Some people with this condition may experience mild epigastric pain, while diarrhea, loss of the body weight and anorexia are quite common symptoms of the bile duct tumors. Other potential symptoms are enlarged liver and distended gallbladder.













Your thoughts on this
Loading...