
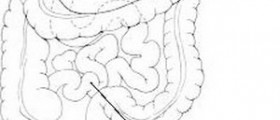
The appendix is a small, sac-like organ, located in the lower right portion of the abdomen. It has no apparent function in the human body, but it does not mean it is not susceptible to complications. Sometimes, due to certain factors, the appendix becomes inflamed and filled with pus, and it is called appendicitis. It causes certain symptoms, the pain being the most prominent one. In many cases, an inflamed appendix must be removed surgically.
This condition can affect anyone, regardless of the age and the sex, but it is most commonly seen in people between the ages of 10 and 30.
Symptoms of appendicitis in children
The main early symptom of appendicitis in all people, including children, is the pain located near the bellybutton. The pain radiates from the bellybutton to the lower right part of the abdomen. There is a method that can be used to determine whether the pain is caused by appendicitis or something else. If sharp pain occurs when the lower right part of the abdomen is pressed with hand and the pressure is quickly released, it is an almost definitive sign the pain is caused by chronic appendicitis.
Another symptom of appendicitis in children is tenderness when the lower right abdomen is pressed. The pain is also aggravated due to actions such as sneezing, coughing, laughing, jumping, walking, running and making other sudden movements.
Alongside the pain, a child with appendicitis may also experience nausea, vomiting, low grade fever, constipation, lack of appetite, inability to pass gas, bloating, diarrhea and similar. Of course, these symptoms are characteristic for other medical conditions too, but combined with the characteristic pain in the lower right abdomen, they probably indicate appendicitis.
Treatment for appendicitis in children
The standard treatment for appendicitis in children is the surgical removal of the appendicitis. The procedure is called appendectomy. The surgery can be an open one, with the incision, or laparoscopic, which involves several smaller incisions. Laparoscopic surgery is today preferred to the open one and it is more widely performed. The incisions from this type of surgery heal faster and the recovery time is much shorter. In some cases, though, a laparoscopic surgery is not possible and the appendix must be removed in an open procedure. The patient usually stays in the hospital a day or two after the procedure.
The symptoms of appendicitis will go away once the inflamed appendix is removed. However, the child should be carefully monitored during the recovery, avoiding strenuous activity, sudden movements, pressure, coughing, if possible, and laughing.









Your thoughts on this
Loading...