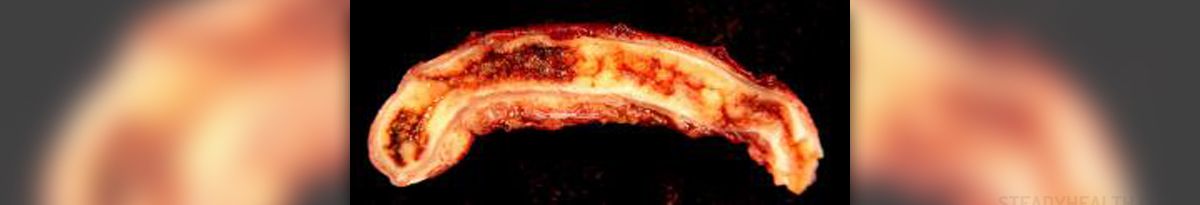
Appendicitis is an inflammation of the appendix, a small organ located on the right side of the abdominal cavity. Appendix resembles a finger, it is attached to the colon and has only one opening, thus resembling a cul-de-sac. As far as the modern science knows, appendix has no specific function in the body and will probably be eliminated in the further evolution process.
The inflammation occurs when food or fecal matter get stuck in the appendix, which then gets infected by bacteria. If the pus-filled appendix bursts, the infection can spread to other organs and cause serious health problems.
Symptoms of appendicitis in adults
Severe pain in lower abdomen is the number one symptom of appendicitis. Other symptoms usually include nausea and vomiting. These are considered early symptoms of appendicitis.
In appendicitis, the pain starts at the belly button and spreads towards the right side of the lower abdomen. The pain gets progressively worse and more sharp, and the area becomes tender if touched. The pain is worse when coughing, sneezing, walking or moving.
The position and severity of pain may depend on the age and general health, but in most cases the pain is located at the right lower abdomen.
Appendicitis may also cause a loss of appetite, nausea and vomiting. Fever occurs very rarely in appendicitis patients, but constipation, bloating and inability to pass gas are more often observed.
The above mentioned symptoms refer to acute appendicitis. There is another form of this condition, chronic or grumbling appendicitis. In chronic appendicitis, what is causing the pain is not infected, but inflamed appendix. The symptoms are similar to those of acute appendicitis, but without nausea and vomiting. Also, the symptoms are less sudden and more gradual.
Treatment for appendicitis in adults
Proper treatment is necessary for either one of the appendicitis types. Proper treatment may be difficult to determine without adequate diagnostic tests. This is because symptoms of appendicitis may resemble those of other diseases and conditions.
Generally, tests that are performed to diagnose appendicitis include X rays, ultrasound, urine and blood tests in laboratory, laparoscopy and CT scan.
The treatment depends on the type and the severity of appendicitis. However, in most cases, especially, in acute appendicitis, the treatment consists in surgical procedure to remove the appendix, called appendectomy.
It is very important to react as soon as the symptoms are observed. The pain caused by appendicitis can be very severe and cannot be ignored, and more importantly, neglecting the symptoms may lead to serious health complications.














Your thoughts on this
Loading...