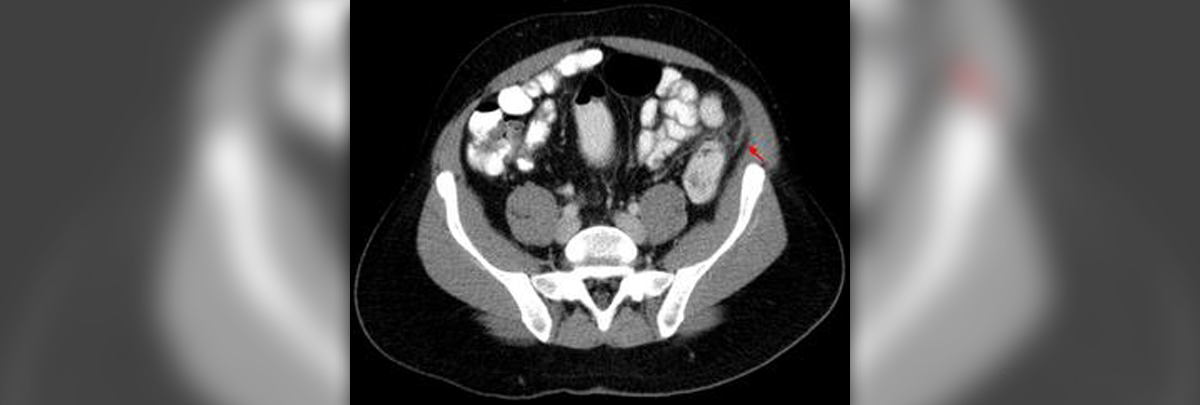
The appendix is a vermiform organ in the human body, like a finger-shaped pouch hanging from the colon, on the lower right part of the abdomen. It has no apparent function in the human body, but that does not mean it is not susceptible to problems. If the appendix becomes inflamed or infected, it is called appendicitis, and it usually has to be removed so the infection does not spread and cause further complications. Laparoscopic surgery is today a surgical method preferred to the traditional one, because it has many advantages like, less scarring and a shorter recovery period.
Appendicitis and appendectomy
Appendectomy is the term used for the surgical removal of the appendix. It is usually done to treat appendicitis, the inflammation and/or infection of the appendix. Appendicitis is an obstruction or an infection of the organ, which can be caused by various factors, such as, trauma, injury, calcified deposits and so on.
Appendicitis causes abdominal pain, which is the most prominent symptom. Other symptoms may include tenderness of the abdomen, especially when laughing or coughing, pain when the area is pressed, nausea, vomiting, diarrhea and low grade fever.
Mild cases of appendicitis can be treated with antibiotics, however, severe cases require surgical removal of the organ, called appendectomy. Appendectomy can be done in two ways- through open surgery or through laparoscopic surgery.
Laparoscopic appendectomy
In a traditional, open surgery, the surgeon makes an incision in the lower right abdomen, where the appendix is located, and examines the appendix and the surrounding organs. He then cuts the appendix from the surrounding tissue and the cecum. The location is sealed, the cecum is returned to its original place and the incision is stitched.
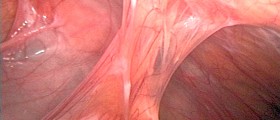
In laparoscopic appendectomy, the surgeon makes three or four smaller incisions in various parts of the abdomen, instead of one large one. The incisions, which are usually one inch long, are made in the lower right abdomen and near the navel. The surgeon inserts a small device with a camera attached to it, called laparoscope, through one of the incisions. The camera allows a clear and precise view and it is used for navigation. The other incisions are used to insert surgical instruments. The abdominal cavity is filled with carbon dioxide and inflated, so the surgeon has enough room. The rest of the procedure is similar to the open surgery.
The advantages of laparoscopic appendectomy include smaller scars due to smaller incisions, faster recovery, less post-operative pain and less chance of complications.











Your thoughts on this
Loading...