
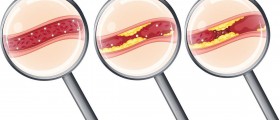
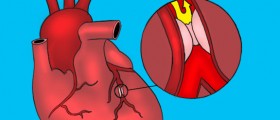
Angioplasty is a technique that mechanically widens a narrowed or completely obstructed blood vessel. Such narrowing or obstruction is a consequence of atherosclerosis. This is a widely accepted and frequently performed procedure and highly efficient means for treating coronary artery disease.
Who Needs Angioplasty
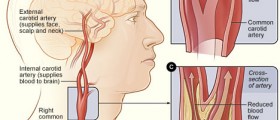
Angioplasty is performed in patients in whom the heart does not receive sufficient amount of blood rich in oxygen due to coronary artery narrowing. The condition per se is highly lethal and may easily progress into heart attack. This is why the goal of the treatment is to widen the narrowed arteries and prevent life-threatening complications.
Angioplasty - Overview
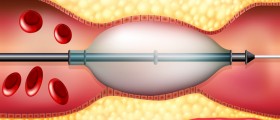
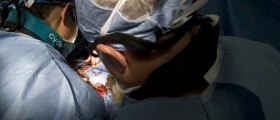
During angioplasty, the affected blood vessels become wider, allowing more blood to enter. This is a great way to once again supply the heart with enough oxygen. The very procedure includes insertion of a thin tube (a catheter) through blood vessels. A well-experienced surgeon leads the tube to the site of narrowing. The tube has a balloon at one end. Once the tube reaches the desirable location, the balloon is inflated. As a result, the plaque gets pushed towards the walls of the artery. This subsequently leads to widening of the treated vessel and restoring the normal blood flow.
After angioplasty patients may remain hospitalized for a day and are then discharged.
Angioplasty - Recovery Time
As it has already been mentioned after the procedure patients stay in hospital for one more day or a couple of days. During this period of time, they are closely monitored.
It is essential to follow doctor's orders, increase fluid intake (maintain proper hydration), and keep both, upper and lower extremities in a straight position. Some patients receive intravenous drugs which prevent blood clotting.
At the site of catheter insertion the skin may be a bit bruised. This skin discoloration soon withdraws. Patients may also report tenderness or even pain at the site of catheter insertion. They are all advised to check the area for potential signs of infection. Excessive redness, swelling or even warmth of the area around the incision site may point to the presence of infection.
Connection Between Heart Attack and Angioplasty
Recovery time for patients in whom the procedure is performed before potential heart attack is shorter comparing to those in whom angioplasty is performed after they have had a heart attack. Patients with previous heart attack require a specific rehabilitation program designed by their doctor.
Finally, after being discharged all patients are given after care tips which they need to stick to while recovering at home.










Your thoughts on this
Loading...