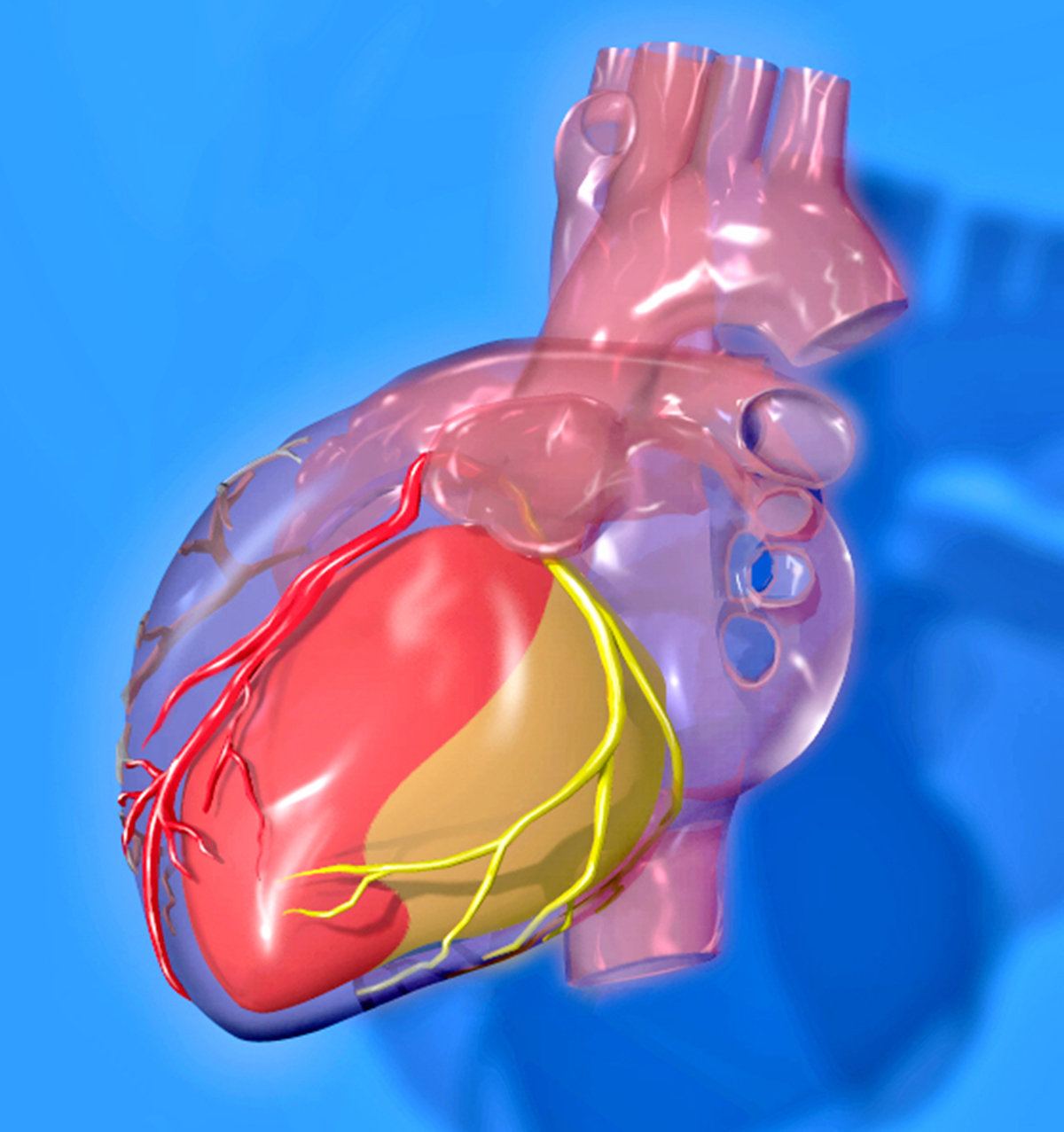
Acute cardiac syndrome or acute coronary syndrome represents sudden reduction of blood flow to the heart. It leads to chest pain and is considered an urgent medical condition. Only if it is diagnosed quickly acute coronary syndrome can be properly treated. In majority of cases the definitive diagnosis is set in an emergency room or a hospital. If coronary cardiac syndrome is not treated on time, it may easily progress into heart attack.
Causes of Acute Coronary Syndrome
Acute coronary syndrome develops as a consequence of gradual build up of plaques in the heart arteries. Such plaques are made of fatty deposits, platelets, fibrin and several more components. They slowly increase in size and lead to narrowing of the affected part of the blood vessel. The effects are detrimental since the blood does not flow in sufficient amounts and the heart muscle suffers from inadequate supply with oxygen and all essential nutrients. In case plaque ruptures it is carried by blood and since it will eventually block the artery it is responsible for heart attack.
Clinical Characteristics of Coronary Syndrome
Symptoms and signs of acute coronary syndrome are actually the same as those of a heart attack. It is essential to recognize these symptoms and signs and treat patient immediately. Only this way heart attack (a further step in untreated acute coronary syndrome) can be prevented.
Typical symptoms and signs of acute coronary syndrome are chest pain (described as burning sensation, pressure or tightness that lasts several minutes or even longer), pain that radiates from the chest to nearby body parts (jaw, shoulder etc.), shortness of breath and heavy sweating. Some patients may suffer from nausea and vomiting.
Treatment for Acute Coronary Syndrome
In case acute coronary syndrome is confirmed patients require prompt treatment. They are administered medications that will reduce the pain and allow the heart to receive more blood. This way heart attack as well as lethal outcome can be prevented. In many cases acute coronary syndrome develops due to angina pectoris and patients are given nitroglycerin. In case heart attack has already developed (and is in early stages) patients require appropriate thrombolytic therapy. Once the condition is brought under control patients may continue taking medications that prevent blood clotting such as Aspirin. Furthermore, those suffering from increased levels of cholesterol in the blood are prescribed with cholesterol-lowering drugs.
Only if medications are not capable to restore the blood flow through the affected heart vessels patients may undergo surgical procedures such as angioplasty and stenting. And finally, severe narrowing requires coronary bypass surgery.












Your thoughts on this
Loading...