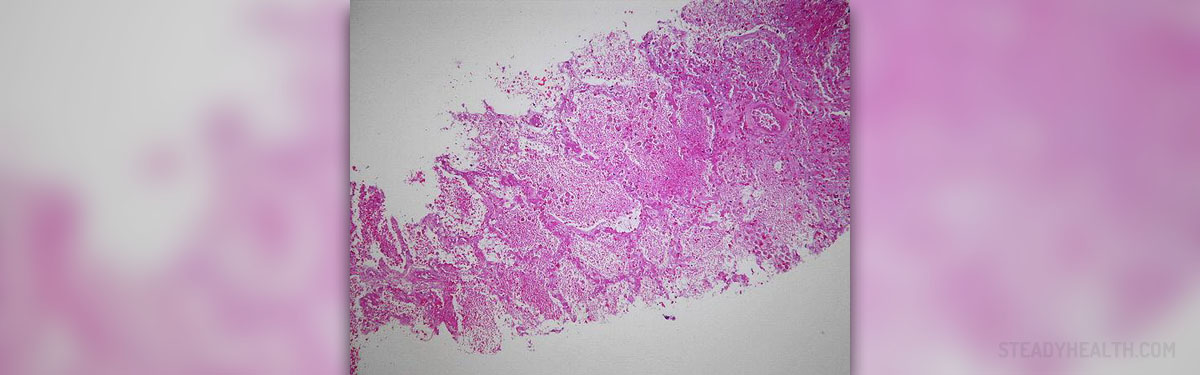
Post-streptococcal glomerulonephritis is inflammation of the kidneys caused by previous infection of the upper respiratory tract or the skin by certain strains of Streptococcus bacteria.
The Onset of Post-streptococcal Glomerulonephritis
Initially, a person develops throat infection or skin infection with a specific type of group A beta hemolytic streptococcus bacteria. During this infection the body produces specific antibodies which may, after short period of time, cause inflammation of the kidneys and induce glomerulonephritis. Affected in such manner, kidneys become incapable of filtrating urine.
In many cases the problems with kidneys develop 1-2 weeks after throat infection and 3-4 weeks after skin infection. It is estimated that post-streptococcal infection most commonly occurs in children between the age of 6 and 10.
Clinical Characteristics of Post-streptococcal Glomerulonephritis
After the kidneys lose their ability to filter urine, an individual suffering from this type of glomerulonephritis experiences obvious decreased urine output. Due to water retention, patients start to develop edema and generalized swelling. The condition may be accompanied by swelling of the abdomen, face or eyes, feet and ankles and the entire extremities. The urine is rust-colored and there may be visibly blood in it.
Additional complaints of people suffering from post-streptococcal glomerulonephritis include joint pain, joint stiffness and swelling.
Diagnosing Post-streptococcal Glomerulonephritis
Blood pressure in such patients is elevated due to water retention. This may be the cause of abnormal sounds during auscultation of the heart and lungs. There are also abnormalities in anti-DNase B test and increase of serum ASO. Serum complement levels are decreased, urine analysis confirms the presence of protein and blood in urine while definitive diagnosis can be confirmed only after kidney biopsy.
Treatment for Post-streptococcal Glomerulonephritis
Unfortunately, there is no specific treatment for this type of glomerulonephritis. This is why treatment is basically symptomatic, i.e. deals with symptoms which patients have developed.
Antibiotics may be prescribed and administered in order to eradicate streptococcal infection that may have stayed somewhere in the body.
Edema and swelling of different parts of the body as well as increased blood pressure may be reduced with blood pressure medications and diuretics. Additional help regarding edema is obtained with dietary salt restriction. Anti-inflammatory medications (like corticosteroids) may be ineffective in case of post-streptococcal glomerulonephritis.Post-streptococcal Glomerulonephritis Prognosis
The inflammation of kidneys usually completely resolves within several weeks or may linger up to several months. In some people, predominantly adults, the inflammation may progress into chronic kidney failure.
Potential complications of post-streptococcal glomerulonephritis include acute renal failure, chronic glomerulonephritis, chronic renal failure, congestive heart failure, pulmonary edema, hyperkalemia, hypertension and nephrotic syndrome.













Your thoughts on this
Loading...