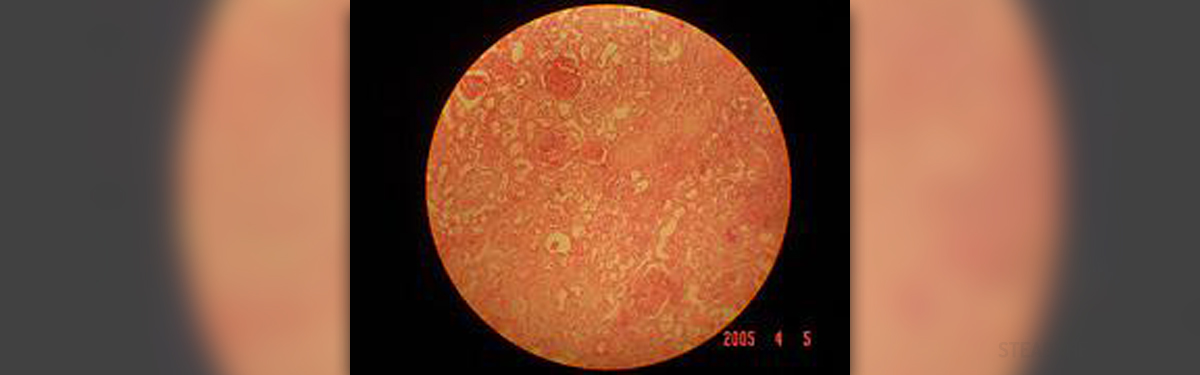
Acute glomerulonephritis is a medical condition affecting the kidneys characterized by inflammation of the internal structures of the organ i.e. inflammation of the glomeruli. A glomerulus is an integral part of the kidney and a participant of the initial filtering of the blood in the process of urine excretion. Each and every glomerulus receives blood from an afferent arteriole of the renal circulation and drains into an efferent arteriole. The process of ultrafiltration occurs thanks to the resistance of the aforementioned arterioles which both contribute to high pressure within the glomerulus. The glomerular filtration rate (GFR) is the rate at which blood is filtered via all the glomeruli in the kidneys and is used to estimate the overall real function.
Causes of Acute Glomerulonephritis
There are several types of glomerulonephritis and acute nephritic syndrome is only one of them and definitely the most severe and damaging type of many different renal syndromes. There is also acute poststreptococcal glomerulonephritis, one of the frequently reported types of the disease.
Acute nephritic syndrome develops as a result of abnormal response of the immune system to some kind of infection or other disease. As a matter of fact acute glomerulonephritis in general develops due to an immunologic mechanism that triggers inflammation and proliferation of glomerular tissue. The inflammation and proliferation are both responsible for damage to the basement membrane, mesangium and capillary endothelium.
The condition is typically characterized by the sudden onset of hematuria (blood in urine), proteinuria (excess of proteins in urine) and red blood cell casts. Additionally, patients develop elevated blood pressure, edemas and if there is a decrease in glomerular filtration (which is often the case), one also suffers from azotemia (abnormally high levels of nitrogen-containing compounds such as urea and creatinine).
As for acute nephritic syndrome the most common conditions that precipitate the onset of the disease in both children and adults include IgA nephropathy, Henoch-Schonlein purpura, hemolytic uremic syndrome and poststreptococcal glomerulonephritis. Apart from the mentioned children may additionally develop the mentioned health problem due to abdominal abscesses, infective endocarditis, pneumonia caused by Klebsiella bacterium and Goodpasture syndrome. Acute nephritic syndrome is also closely connected with hepatitis, membranoproliferative glomerulonephritis type I and II, lupus nephritis, syphilis, typhoid fever and several other diseases.
All in all, once the glomeruli get inflamed the kidneys stop filtering the blood and waste products are not eliminated adequately. Also, there is significant water retention blamed for swelling of various body parts and congestion or many organs. The urine is secreted ether in small amounts or one develop anuria. And finally, damage to the kidneys leads to bleeding and the presence of blood in urine.
Treatment for Acute Glomerulonephritis
Treatment is adjusted according to the underlying condition, the culprit of glomerulonephritis and the symptoms patients have to deal with. For instance, individuals suffering from poststreptococcal glomerulonephritis basically require supportive care. More severe cases of acute glomerulonephritis such as patients who have developed hypertensive encephalopathy or pulmonary edema are treated in intensive care units. It is essential to monitor renal function, blood pressure, serum albumin and urine protein excretion rate as well as the total output of urine. Many medications may improve patient's condition and help them with the associated problems.
As far as the prognosis is concerned, it basically depends on the very disease that have led to glomerulonephritis in the first place. In case the underlying illness is brought under control, problems regarding blood pressure and fluid retention may significantly improve within the following 1-2 weeks. Urine test, however, may remain abnormal for several months. The recovery is better in children. Complications including end-stage kidney disease and chronic form of the disease predominantly affect adults.
Medications for Acute Glomerulonephritis
First of all, patients with infections require antibiotics. Antimicrobial agents may sometimes prevent poststreptococcal glomerulonephritis from developing.
Furthermore, loop diuretics are essential for all patients who have elevated blood pressure and in whom water retention resulted in edema. These drugs efficiently eliminate excess of fluids from the body.
Also, severe cases of hypertension induced encephalopathy are treated with vasodilator drugs such as nitroprusside, nifedipinem hydralazine etc.
Glucocorticosteroids may be of additional help when the abnormal reaction of the immune system is rather severe which is sometimes seen in, for example, poststreptococcal glomerulonephritis.
Apart from medicamentous therapy, all patients must stick to specific dietary changes. Namely, since the body is already prone to sodium and water retention, there are restrictions of both in one's diet. In azotemic patients intake of proteins should be limited as well. Bed rest is a must. Light activities are allowed only once glomerular inflammation subsides and circulatory congestion withdraws. Doctors will decide when patients may start with every day activities and what they should abstain from during the recovery.
And finally, since older individuals are prone to chronic sequelae and they generally develop complications more compared to children, they require more attention and should be closely monitored.














Your thoughts on this
Loading...