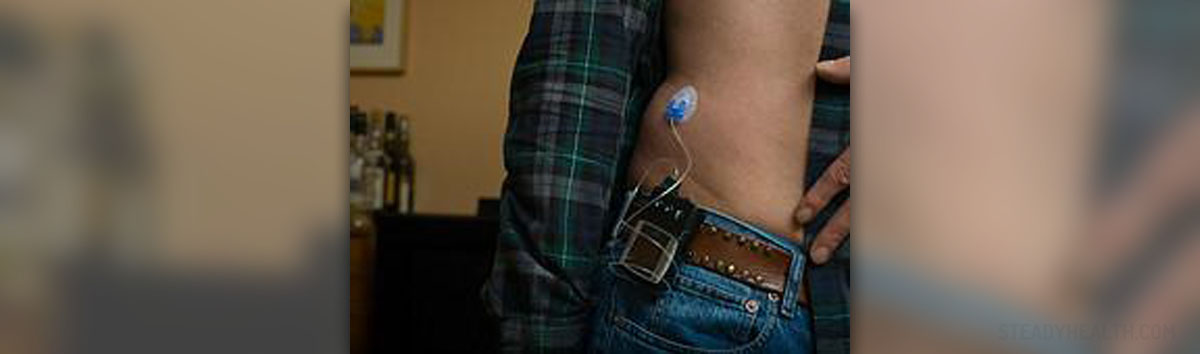
Insulin pumps are devices used in treatment of diabetes mellitus. Diabetes is a chronic disease which develops due to failure of the pancreas gland to produce enough of insulin required for normal blood sugar levels. It is a common disease that affects millions of people worldwide. Diabetics require life-long insulin therapy which helps them to maintain the blood glucose in the targeted range.
How Can Insulin Be Supplemented
Insulin can be supplemented by different means. Insulin tablets are almost out of the industry. Insulin injections are commonly used but downside of this mode of administration is that it requires a diabetic to correctly take his or her meal and schedule the therapy.
The insulin pumps, on the other hand, provide better absorption of insulin by the body and constantly deliver insulin in small amounts instead of large amounts a few times a day. Insulin pumps act by mimicking the pancreas from outside the body.
Insulin Pumps Overview
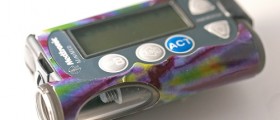
The insulin pump is a small device about the same size as the cell phone. It is worn around the waist, attached to the belt or in the pocket. The insulin pump is composed of a pump with different controls, processing module and battery for charging the pump. A disposable reservoir for insulin is inside the pump and there is also a disposable infusion set which includes a cannula and tubing system. The cannula is inserted under the skin (on the abdomen) to deliver insulin directly into the blood stream while the tubing system links the reservoir with the cannula. How Insulin Pumps Work?
Insulin pumps deliver insulin in two ways. A basal dose continuously distributes insulin between meals and at night to maintain blood glucose levels. A bolus dose passes large amounts of insulin before meals or to correct high glucose levels in blood. Generally, the insulin pumps deliver rapid-acting insulin in a constant flow.
Pros and Cons of Insulin Pumps
Unlike other modes of administration, insulin delivered via pump is more convenient and offers better quality of life. Diabetics do not have to worry about their meal and therapy schedule. The amount of delivered insulin is precisely measured thus diabetes management is simplified. The pumps are also suitable for insulin dependent infants.
On the other hand, a diabetic must wear his or her insulin pump at all times in order to maintain normal blood glucose levels, which may be inconvenient if he or she is engaged in sport or any other activity that involves rough moves. There is a risk of diabetic ketoacidosis if the pump battery discharges, the reservoir gets empty or components of the pump malfunction. Thereby, the users have to be well-informed about the pump and its usage.












Your thoughts on this
Loading...