Diabetics are more than any other group of people susceptible to retinopathy. Diabetes type 1 is a medical condition caused by inability of the body to produce insulin, while type 2 of the same disease is associated with production of inadequate amounts of this hormone (insulin) or lack of response of the body to the existing insulin. Type 1 diabetes is usually diagnosed in teenagers or people under 40 years of age, while type 2 is more often linked to older people (over 45 years of age).
Both of these patients may develop different medical problems if their blood sugar (glucose) level is not brought under control, either by medications or insulin, depending on the type of this disease.
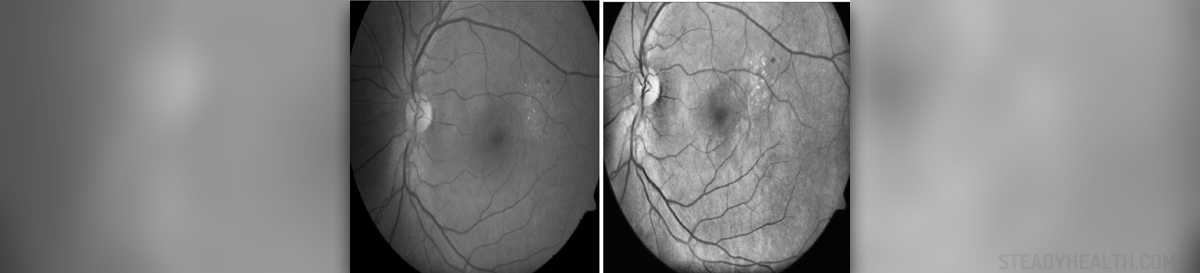
Retinopathy in Diabetic Patients – What to Expect?
As said, diabetics may have various medical problems because of their condition. High blood sugar is known to cause damage to many organs in the body, including the eyes. These patients may develop diabetic retinopathy and this eye problem is found to be very frequent in poorly managed or untreated diabetes. About 25% of people diagnosed with type 1 diabetes are estimated to develop diabetic retinopathy within the period of 5 years and the same goes for patients suffering from diabetes type 2. However, if these patients (type 2 diabetes) require insulin, the risk is much higher because about 40% of them develops diabetic retinopathy and may end up with permanent loss of vision.
Diabetic retinopathy is considered to be the leading cause of vision loss and blindness in adult patients younger than 65 years of age. Early treatment can prevent some 90% of all cases of severe vision loss. It initially involves better control over the blood sugar level, while later stages of diabetic retinopathy usually require laser surgery to repair vision.
Diabetic Retinopathy Complications
Even on its own, diabetic retinopathy is a bad sign, showing that the level of blood sugar is not controlled properly. This condition may also complicate further and lead to more severe medical problems, like growth of blood vessels in the retina, problems with the blood flow in the eye, but also some bleeding inside the eye, traction retinal detachment or neovascular glaucoma.
Vitreous hemorrhage (bleeding in the eye) may be mild or more serious, leading to some temporary vision problems or complete loss of vision. Most patients do not experience any permanent loss of vision and the problem resolves after several weeks or months.
Tractional retinal detachment and neovascular glaucoma are more serious complications of diabetic retinopathy and they might lead to complete and permanent loss of vision.
















Your thoughts on this
Loading...