What is folliculitis?
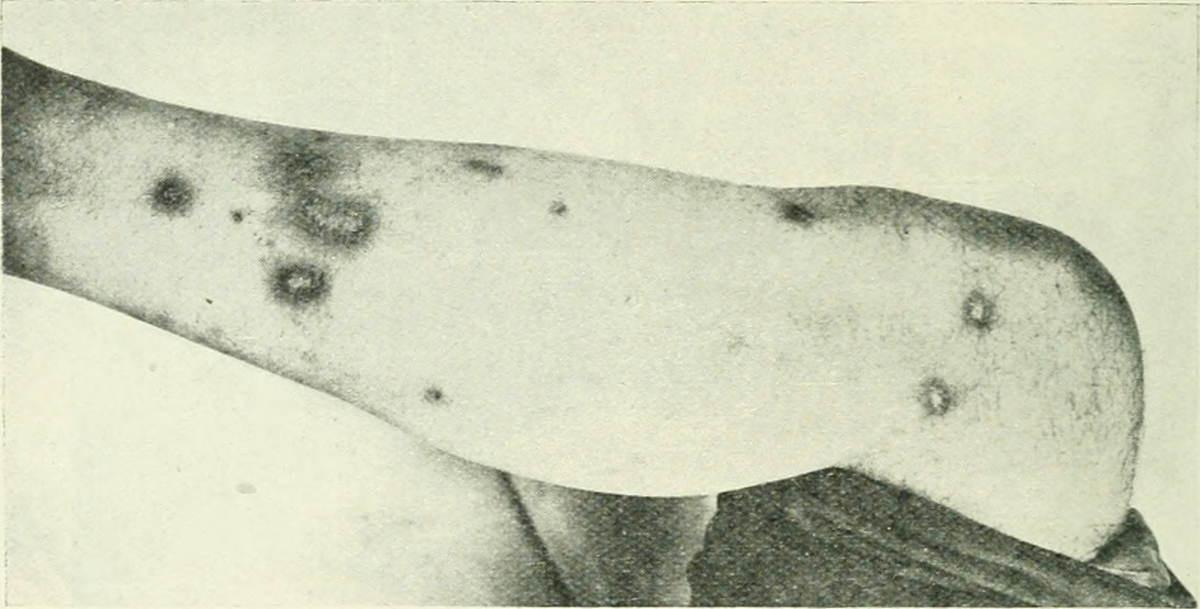
Folliculitis is a common skin condition characterized by the inflammation of hair follicles. It looks like small red bumps scattered on the skin, usually on the chest, back, arms, neck, legs, buttocks and face. Even though it may resemble acne, folliculitis is not the same thing.
The red bumps on the skin may be itchy or painful and they always look inflamed. If a bump is scratched open, it may reveal a small coiled or trapped hair that has not grown out.
Folliculitis can affect anyone, although it is commonly seen in adolescents. It is generally not associated with any other medical condition. However, people with compromised or weakened immune system are more likely to suffer from it.
Razor burn folliculitis
Razor burn folliculitis, just as the name suggests, is associated with shaving. In women, it is common on the legs, while in men it can be seen on the chin and the cheeks. Repeated tiny cuts made by the razor on the skin cause tiny openings, which allow the bacteria to invade deeper follicles, resulting in inflammation. In addition, close shaving may cause the hair to remain trapped underneath the skin, which is also considered to be folliculitis.
Treatment for folliculitis
Folliculitis often clears on its own, without any particular treatment, especially in mild cases. However, some people chronically suffer from folliculitis and they are advised to seek medical attention and get treated.
The treatment for folliculitis will depend on the underlying cause and on the specific type of folliculitis. Razor burn folliculitis can be treated by changing the shaving habits, for example using depilatory creams, wax or electric razors. The manner in which a person shaves also plays a role.
For mild bacteria folliculitis the treatment may consist of over-the-counter antibacterial washes based on benzoyl peroxide or chlorexedine. These washes should be used twice a day, in the morning and in the evening, and for best results they can be combined with topical ointments containing antibiotics.
Moderate and severe cases of folliculitis require more serious treatment, usually combining Topical antibiotic ointments or lotions, such as clindamycin or metronidazole, with oral antibiotics, which may include cephalexin, dicloxacillin, doxycyline, tetracycline and such, especially if folliculitis is more resistant.
After the condition clears with the use of oral antibiotics, it is recommended to maintain healthy skin by using antibacterial washes and lotions on a regular basis.
Fungal folliculitis, which is less common than the bacterial type, is treatment with anti-fungal shampoos or body washes, twice a day, or, in severe cases, with topical anti-fungal creams and oral medication.

















Your thoughts on this
Loading...