
Infected hair follicle is a condition medically referred to as folliculitis. It is actually an inflammatory condition which affects the hair follicles. Most cases of infected hair follicles involve a certain type of bacteria which is known as staphylococcus aureus. This is why the condition is also sometimes referred to as the staph infection of the hair follicles. Other common causes of infected hair follicles include prolonged contact of the skin with plastic dressings, wounds from a surgery, skin abrasions, dermatitis, acne, over-sweating, shaving and wearing tight clothing.
Infected Hair Follicle Symptoms
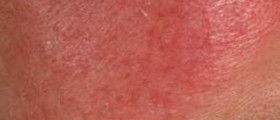
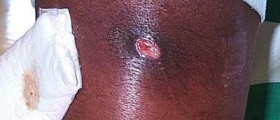
Symptoms of infected hair follicles are commonly determined by the cause of the actual condition. Folliculitis may be superficial or deep. Superficial folliculitis types include herpetic folliculitis, pityrosporum folliculi, pseudofolliculitis barbae, tinea barbae, pseudomonas folliculitis and staphylococcal folliculitis. Herpetic folliculitis is characterized by small blisters filled with fluid, pityrosporum folliculi is characterized by red itching pustules on the back, chest, neck, upper arms or face, pseudofolliculitis barbae is characterized by swelling and dark raised scars on the face and neck, tinea barbae is characterized by itchy, white bumps on the beard area, pseudomonas folliculitis is characterized by red itchy bumps and the staphylococcal folliculitis is characterized by white itchy bumps filled with pus. Deep folliculitis types include eosionophilic folliculitis, skin boils and carbuncles and also gram-negative folliculitis. This type of folliculitis is characterized by pus filled sores, blisters filled with pus and painful sensations. Scars are a very common thing after this type of condition.
Infected Hair Follicle Treatment
Eosinophilic folliculitis is commonly treated by a course of oral corticosteroids. Boils and carbuncles can be treated simply by a small incision in the affected area, which commonly provides relief from pain and accelerates the recovery. The area also needs to be covered with sterile gauze so that the pus stops draining. Some cases may also involve a course of antibiotics. Gram-negative folliculitis is also commonly treated with antibiotics. Herpetic folliculitis usually does not require any specific type of treatment. Pityrosporum folliculi is commonly treated either with oral or topical antifungal medicaments. Pseudofolliculitis barbae is a type of folliculitis which involves switching to electric razor from the razor blade. Shaving gel should be used instead of shaving cream. Tinea barbae is commonly treated with oral anti fungal types of medicaments. Pseudomonas folliculitis does not require any specific type of treatment. Severe cases may involve oral antibiotics. Staphylococcal folliculitis is commonly treated with oral or topical antibiotics.














Your thoughts on this
Loading...