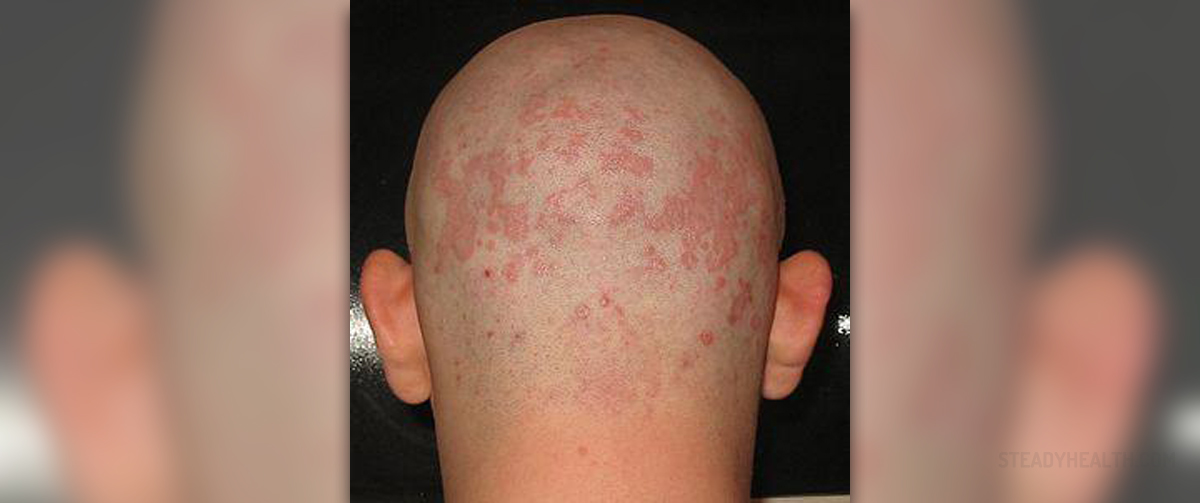
Seborrheic dermatitis is a skin condition that commonly affects the scalp, but can be seen on other parts of the body as well. Though seborrheic dermatitis is associated with increased activity of the sebaceous glands, which are glands located in the skin that secrete sebum, the exact mechanism behind its cause hasn't yet been identified. Sebum is a natural oily substance that crates a thin coat on the skin, protecting it from microorganisms and lubricating it.
Seborrheic dermatitis, characterized by redness, dryness, scaling, flaking, itching, and persistent dandruff, has been linked to several possible risk factors. Fungal causes have been identified in many cases as being responsible for seborrheic dermatitis. In this case, the symptoms are in fact an inflammatory reaction to a fungal species, usually those of Malassezia type.
Other risk factors for seborrheic dermatitis are associated with genetics, environment, overall health and the nature of the immune system; people with weakened immune systems are more likely to suffer from seborrheic dermatitis, as are those who are under a lot of stress. Even certain medications appear to be capable of triggering seborrheic dermatitis.
Seborrheic dermatitis of the body
Seborrheic dermatitis is usually found in sebum-rich areas of the body. This condition mainly affects the scalp, causing dandruff. However, it can affect other parts of the body as well, like the face, the chest and the back, shoulders and upper arms, particularly in areas that are naturally more oily, such as the ears, the folds around your nose, your eyelids, or the area underneath female breasts.
Basically any skin fold or any part of the body that is particularly oily due to too much sebum can be affected by persistent scaly patches. Seborrheic dermatitis is also commonly seen on hairy parts of the body, where it affects hair follicles and causes inflammation. In those parts of the body, this skin condition can cause hair loss, which is usually temporary, although in severe or recurring cases the hair loss can be permanent too.
Treatment for seborrheic dermatitis of the body
Since seborrheic dermatitis is a condition that primarily affects the scalp, most medications for seborrheic dermatitis are designed to treat skin inflammation of the scalp, or dandruff. However, there are also very effective solutions for seborrheic dermatitis on the other parts of the body.
The active ingredients used in most topical solutions for seborrheic dermatitis are antifungal agents, corticosteroids and calcineurin inhibitors. These treatments for seborrheic dermatitis are usually offered in form of shampoos, body washes, lotions and ointments. Some treatments for seborrheic dermatitis are mild and suitable for everyone — and those treatments are available over the counter — while others treatments for seborrheic dermatitis are more concentrated and stronger, and those are only available by prescription.
Products advertised as treatments for seborrheic dermatitis may also include salycilic acid, coal tar, selenium sulfine and zinc pyrithione.
A natural therapy or alternative treatment for seborrheic dermatitis of the body may involve aloe vera, tea tree oil, coconut oil, honey and avocado. Some of these compounds have proven antimicrobial properties, but be aware that natural treatments do not always work and can also have side effects of their own. When too concentrated, for instance, tea tree oil can cause stinging and irritation. There is some evidence that phototherapy may also help to manage seborrheic dermatitis, especially with recurring outbreaks of seborrheic dermatitis.














Your thoughts on this
Loading...