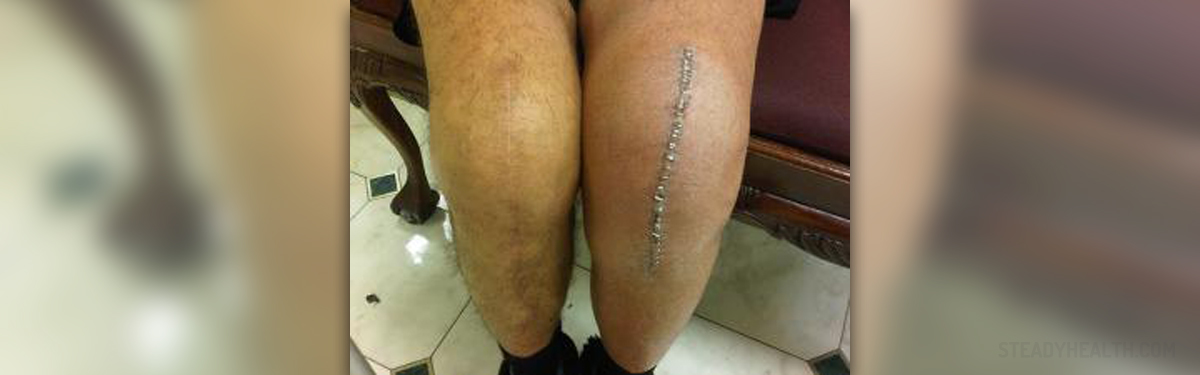
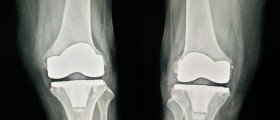
What Is Total Knee Replacement?
A total knee replacement is a surgical procedure in which the damaged knee joint is replaced with artificial material. The knee is a hinge joint and it is essential for motion at the point where the thighs meet the lower legs. During the procedure the distal part of the femur (the thigh bone) is removed and replaced with a metal shell. The end of the tibia (the lower leg bone) is also removed and replaced with a channeled plastic piece with a metal stem. The posterior cruciate ligament is a structure that stabilizes each side of the knee joint. During total knee replacement the posterior cruciate ligament may be retained, sacrificed or substituted by a polyethylene post.
Who Is a Suitable Candidate for Total Knee Replacement?
Total knee replacement is a surgical procedure performed on people whose knee joints are severely damaged and have lost most of their function. The damage to the joints is caused by many inflammatory conditions such as progressive arthritis and it may also develop as a consequence of a repeated injury or trauma to the knee. The most common cause of serious damage to the knee joint in the United States is osteoarthritis of the knee.
People in whom the knee joint has lost its function, those who suffer from progressive and intensive pain in the particular joint as well as people whose knee joint is stiff, are perfect candidates for the surgery. Only the doctor may recommend the surgery and he/she must inform patients about all the benefits as well as potential complications and side effects of the surgery.
What Are Risks Associated with Total Knee Replacement?
Patients who undergo total knee replacement are at a higher risk for blood clots. Clots form inside the veins in the legs and they may travel to the lungs and cause pulmonary embolism. Pulmonary embolism features with shortness of breath, chest pain and in severe cases shock. Furthermore, patients may develop urinary tract infection and several more infections. Pain and swelling of the operated area are normal body's reactions to the surgery and they withdraw with pain killers or spontaneously. In some cases there may be serious complications such as chronic knee pain, stiffness of the knee joint, bleeding into the knee joint, nerve damage, blood vessel injury and infection of the operated site. Some patients develop allergy to certain medications given as a part of anesthesia. Fortunately, most of the previously mentioned complications can be successfully prevented and even if they occur they are adequately treated.







Your thoughts on this
Loading...