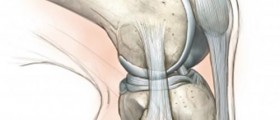
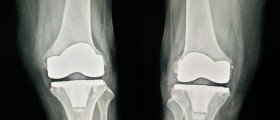
Partial knee replacement is considered a rather good option for patients suffering from certain conditions of the knee such as osteoarthritis of the knee joint. The procedure is also known as unicompartmental knee arthroplasty. Comparing to total knee replacement surgery, partial knee is less invasive, includes smaller incisions and the recovery time is shorter.
Benefits of Partial Knee Replacement
Partial knee replacement surgery is a minimally invasive surgery where only the damaged parts of the knee cartilage are replaced. In early stages of osteoarthritis when only parts of the knee cartilage are damaged, partial knee replacement is the best suitable surgical option.
The only disadvantage of the surgical procedure is that it simply cannot be performed if large portions or the entire cartilage have been destroyed. If this is the case a patient must undergo total knee replacement surgery. And finally, the recovery time after partial knee replacement surgery is much shorter comparing to more invasive total knee replacement surgery.
Partial Knee Replacement - Recovery Time
The recovery time after partial knee replacement is between 6 and 8 weeks. The patients are suggested to use crutches during this period. The operated knee must be spared from any pressure which may interfere in proper healing.
After the surgery the patient's mobility is significantly reduced, at least during the first couple of weeks of the recovery period. Regular and not so strenuous daily activities are allowed 8 weeks after the surgery. Right after the surgery the knee is supposed to be held elevated and in case of pain patients are prescribed pain relieving medications. The doctor decides when is the most convenient time for a patient to engage in a physical therapy. This treatment modality increases the strength of the knee muscles and restores all the movements in the knee joint.
There are several potential complications associated with partial knee replacement and they include instability of the knee, implant loosening, deep implant infection, nerve injury, injury of the popliteal artery, and problems with wound healing, hematoma, pain and decreased range of motion.








Your thoughts on this
Loading...