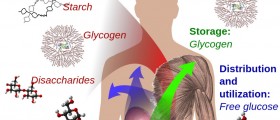
Diabetes (Diabetes Mellitus) is simply caused due to too high level of sugar in human blood. This happens when there is not enough insulin produced from one’s pancreas (also type 1), or because of the wrong or incomplete response to produced insulin by the cells in human body (type 2). There are other forms of diabetes like gestational diabetes (happens to some pregnant women because of high sugar level during pregnancy), congenital diabetes (genetically related), monogenic diabetes and others…
Classification:
Type 1 diabetes occurs with a loss of the beta cells (pancreatic cells responsible for producing insulin). This type of diabetes can be immune mediated and idiopathic. There is no way to predict or prevent this type of disease and it can strike at any age. The cause of type 1 is unknown, and onsets when loss of beta cells causes T-cell related autoimmune attack.
Type 2 diabetes is caused by insulin resistance and is the most common type. During the first stage of this disorder, the level of sugar in blood can be controlled with medications. As the condition progresses, it is harder to control the sugar level in blood without a therapeutic insulin replacement. The cause of type 2 is, at a large level, related to lifestyle.
Gestational
This type of diabetes occurs in 2-5% of all pregnancies. This kind of diabetes is treatable, but, up to 50% of women who suffered this type of diabetes during pregnancy will develop type 2 diabetes during their lives.
Symptoms:
Polyuria (frequent urination), polyphagia (increased hunger) or polydipsia (increased thirst), are the most common symptoms. Symptoms that can develop later are related to blood vessels damage caused by increased glucose. These symptoms can be partial or full eyesight loss, breathing problems, abdominal pain, nausea, vomiting, rashes and damage of capillaries.
Diagnosis:
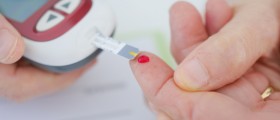
Diabetes is diagnosed by blood tests. These tests are glucose related.
Treatment:
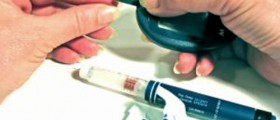
First of all, it is important to control glucose level in your blood. Your glucose-meter should help you know your glucose level. Also, A1C tests, applied twice a year will give you the average result for the past three months. It is important to keep your glucose level below 6, but to avoid too low level. These data can help your doctor to give you an advice what kind of diet and activity plan you should use.
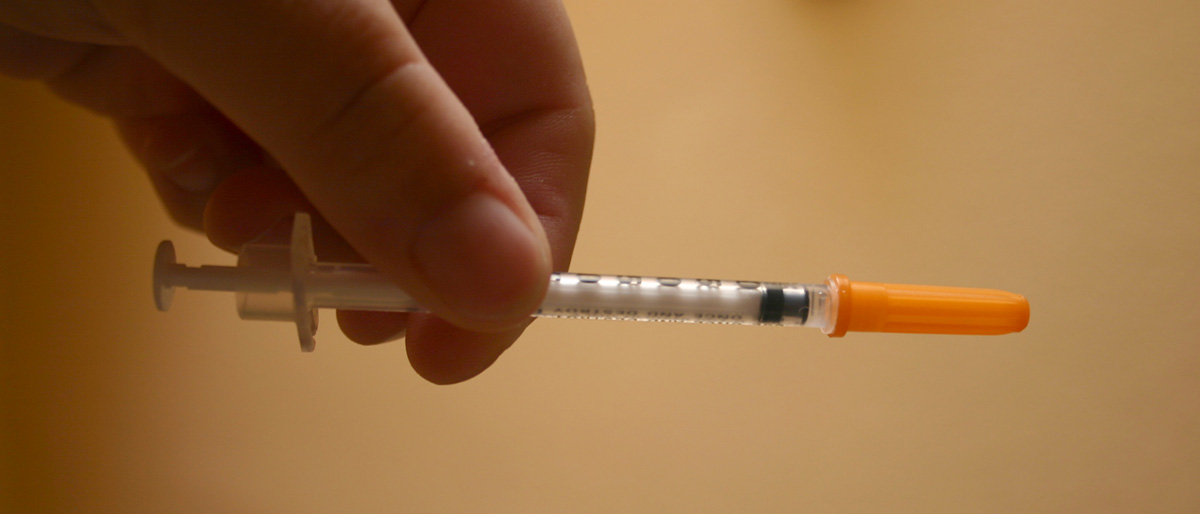
If you have type 1 diabetes, your therapy should consist of insulin, because there is not enough of it produced by your body. For type 2 diabetes, there are several drugs like metformin. Type 3 diabetes needs increased physical activity and better diet, but some women may need insulin.
Insulin may be applied intravenously by an injection, jet injection, or a pump. Your doctor will decide what way of insertion and an amount of insulin you should use. There are also pills for treating diabetes and non-insulin injections, which work with body's or injected insulin.












Your thoughts on this
Loading...