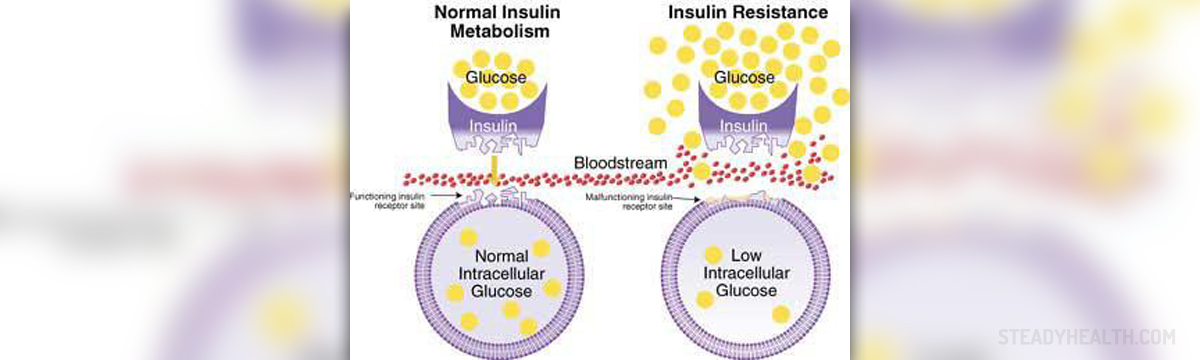
Insulin resistance is a condition that develops when the body cells become resistant to the effects of insulin. Insulin is a hormone produced by the pancreas. Insulin helps to transport glucose into cells where it is converted into energy. In case of insulin resistance, when cells fail to respond to insulin, glucose levels start to increase in the blood and the body responds by producing more insulin. In time, this can lead to a state of hyperinsulinemia, featured by elevated levels of insulin in the blood. Insulin resistance is not a disease but it is associated with several health problems. Insulin resistance can either cause or be caused by medical conditions such as cardiovascular disease, hypertension, type 2 diabetes, obesity, fatty liver and polycystic ovarian syndrome.
Causes of Insulin ResistanceThere are several possible causes of insulin resistance. In some people, insulin resistance can be present at birth (congenital insulin resistance). In most cases, it develops due to genetic predisposition or because of an unhealthy lifestyle. Lack of physical activity can be responsible for development of insulin resistance. Medical conditions that can lead to the condition include: metabolic syndrome, obesity and infections. Pregnancy, stress and use of drugs like steroids can also trigger insulin resistance.
Complications of Insulin Resistance
Insulin resistance can cause many health problems. It can lead to metabolic syndrome, a term used for number of conditions that occur together. They include: high blood pressure, high triglycerides, low HDL (good cholesterol) and excess body fat around the waist. Metabolic syndrome increases the risk for cardiovascular disease and type 2 diabetes. Metabolic syndrome can cause diabetes because of increased levels of glucose. Heart disease can be caused by metabolic syndrome due to high blood pressure and high cholesterol that contribute to build up of plaque in arteries. People with metabolic syndrome are typically insulin resistant. Risks for both metabolic syndrome and insulin resistance increases with age. Overweight people, particularly people with abdominal obesity are especially at risk. According to one study, around 10% of young adults and 44% of people above 60 years of age suffer from metabolic syndrome. In case of insulin resistance, the percentage is much higher.
Signs and Symptoms of Insulin ResistanceInsulin resistance is in most cases asymptomatic. However, several signs and symptoms can indicate presence of the condition. They include: high blood pressure, increased levels of blood triglycerides, high blood sugar, weight gain, intestinal bloating, sleepiness, fatigue, increased hunger, depression and difficulty focusing.









Your thoughts on this
Loading...