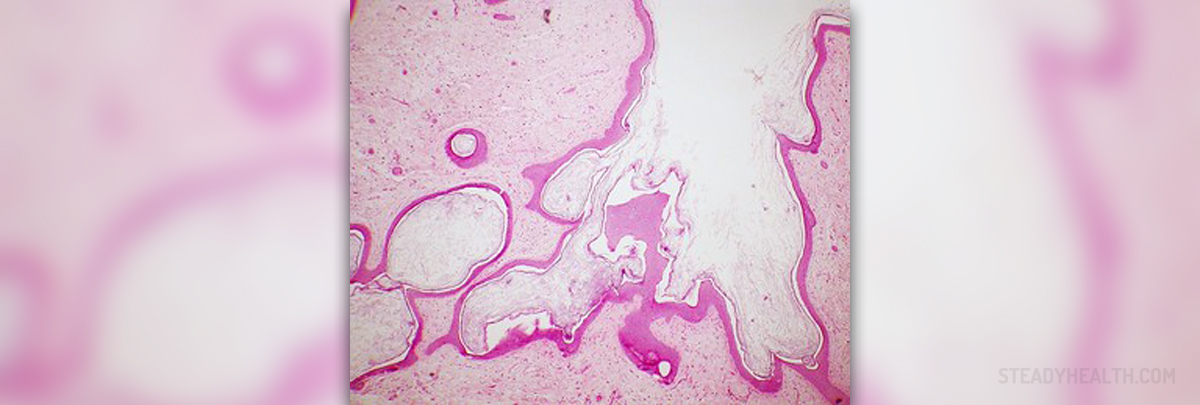
Ovarian dermoid cysts can start developing in woman's ovaries during her fertile years. They are most frequently diagnosed in young women around 30 years of age. Ovarian dermoid cysts are the most common abnormal growth found in girls under 20 as well. These cysts tend to be smaller than 10 cm in diameter, but can grow beyond 15 cm in some cases. In the long-term, dermoid cysts can cause infection, ovarian rupture, torsion and even cancer.
Symptoms
The main symptoms of an ovarian dermoid cyst are abdominal, pelvic and lower back pain. A woman's menstrual period may be especially uncomfortable, and sex can become unpleasant too for those who have these cysts. Ovarian dermoid cysts can cause problems with urination, sudden weight gain and constant nausea (without vomiting) too. Bleeding in between period is also not uncommon. Unfortunately, these same symptoms are common to many female pelvic problems, including Pelvic Inflammatory Disease and other types of cysts. If you recognize yourself in this list of symptoms, a trip to the doctor is certainly necessary but don't self-diagnose "teeth in the ovaries" just yet!
Treatment
Ovarian mature teratoma is cured with surgery. These cysts are usually diagnosed through pelvic ultrasound followed by a CT scan, but in more difficult cases a pelvic MRI can be requested. Ovarian dermoid cysts can be removed through conventional surgery, but laparoscopic surgery may be a less invasive option available at most hospitals these days.











Your thoughts on this
Loading...