What Causes Ovarian Cysts?
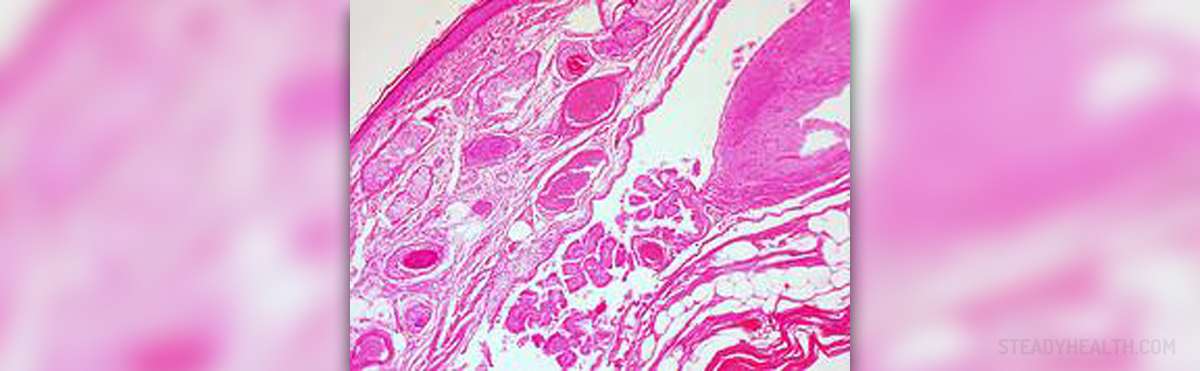
A cyst in the ovaries is a pouch filled with fluid surrounded by a thin wall. Such an occurrence which is smaller than two centimeters is not considered a cyst. Ovarian cysts can be as little as peas or as big as oranges. In most cases cysts are fairly harmless and generate no symptoms. On the other hand, some cysts can cause serious health complications if they burst, leading to internal bleeding and severe pain. Large cysts which can trigger serious problems are surgically removed. Cysts are a relatively common occurrence given how they are usually created. Ovaries are organs which produce and store eggs until they are ready to be released and possibly fertilized. In most cases only one ovary is active each month producing an egg which is stored in a follicle. Once the uterus is ready to house an egg it is released and travels through the fallopian tubes. Every month the uterus creates a thick wall that is supposed to care for the fertilized egg. In case the egg does not get fertilized it travels through the reproductive organs and out of vagina together with the lining of the uterus in a form of menstrual blood. A cyst is created in case the follicle fails to burst and remains in the ovary.
Via image scanning, cysts appear like bubbles and usually affect only one ovary. In addition, ovarian cysts can appear in women of all ages and are in most cases functional, i.e. are created though a natural process and do not pose any harm as they are not part of any underlying anomaly. There are many instances in which the cyst bursts and disappears without any kind of therapy, and sometimes even without the woman being aware of its existence. It should be noted that ovarian cancer sometimes contains cysts but the cysts are usually free of any cancerous cells.
Types of Ovarian Cysts
Although the creation of ovarian cysts is relatively simple there are numerous kinds which can be found in women during reproductive years. For instance, corpus luteum cyst is a type of cyst that does not refer to the egg but to the follicle once the egg has been released. In most cases as a pregnancy does not occur the follicle, which is now the corpus luteum, degenerates and disappears, but there are those rare instances in which the sac fills with liquid and stays in the ovary in which it was created. T
The follicular cyst, on the other hand, is a kind of cyst which is created if the ovulation does not occur and the follicle grows until it becomes large enough to be considered a cyst. Contrary to the corpus luteum, when the follicular cyst burst it triggers pain before it subsequently disappears within a couple of months. Further, the hemorrhagic cyst is characterized by bleeding inside the follicle which is accompanied by sharp pain.
Another kind of cysts known as endometrioid cysts occurs when there is the lining of the uterus present on the ovaries, and it usually affects women in their childbearing years. The endometrioid is a painful cyst but the pain that it causes is usually not distinguished from the menstrual pain. Endometriosis is a condition in which the tissue from the uterus is found outside it and usually leads to infertility until the excess tissue is removed.
In addition, polycystic ovaries occur as a result of the presence of more than one cyst. Also, in polycystic ovaries the cysts are larger than normal while some smaller ones are located outside the ovaries themselves. Polycystic ovaries are different from polycystic ovarian syndrome (PCOS) which is a condition accompanied by cardiovascular and metabolic issues. The PCOS is characterized by heavy bleeding, miscarriages, problems during pregnancy, and sterility. The syndrome is relatively common as it affects almost 10 percent of women in their reproductive age. Further, there is a type of benign tumor called cystadenoma, which is created from the ovarian tissue and can be as big as 12 inches in diameter.
Lastly, the dermoid cyst is considered to be a begin tumor and usually affects younger women. The dermoid cyst can consist of other tissue such as bone, hair, or fat. Most of these cysts are diagnosed through CT scans, MRIs, or ultrasounds. A complication which can commonly occur with any of the cysts is their twisting which usually results in abdominal pain.
Complex Cyst Problems
Some of the commonly observed problems when it comes to ovarian cysts include ovarian torsion. If the cyst becomes large enough it can cause the ovary to move from its original position in the pelvis. Consequently, the moving of the ovary or its torsion results in a lot of pain. Another kind of complication associated with ovarian cysts is their rupture. When a cyst bursts inside an ovary it can cause internal bleeding and pain if it was large enough to begin with.










Your thoughts on this
Loading...