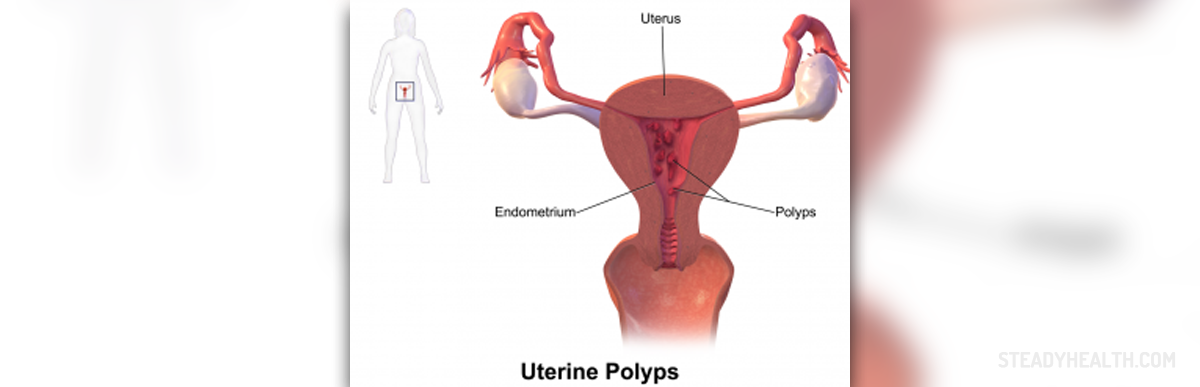
Uterine polyps typically occur in older women, but they can form in younger women too. The exact cause remains unknown, though hormones certainly play a role. There are not always symptoms, but when symptoms do appear, the most common one is abnormal bleeding, both during menstruation (women with uterine polyps might have heavy and more painful periods) and during the rest of the month. It is also possible that uterine polyps impact the regularity of a cycle. Women with polyps could have frequent periods, or prolonged periods (see period lasting for two weeks? for example).
In some cases, uterine polyps can lead to infertility. If you have noticed any or all of these symptoms, making an appointment with your doctor is advisable. Risk factors include hypertension and obesity, but uterine polyps can occur without risk factors as well. They are diagnosed through an ultrasound, normally carried out trans-vaginally. They can be removed surgically, or with the help of hormonal medication. In some cases, uterine polyps are cancerous or pre-cancerous. If this is not the case, and the patient is not trying to get pregnant, a "wait and see" approach can also be adopted. Sometimes, uterine polyps go away on their own. When the polyps are cancerous (which is established through a lab culture), a hysterectomy is sometimes carried out.













Your thoughts on this
Loading...