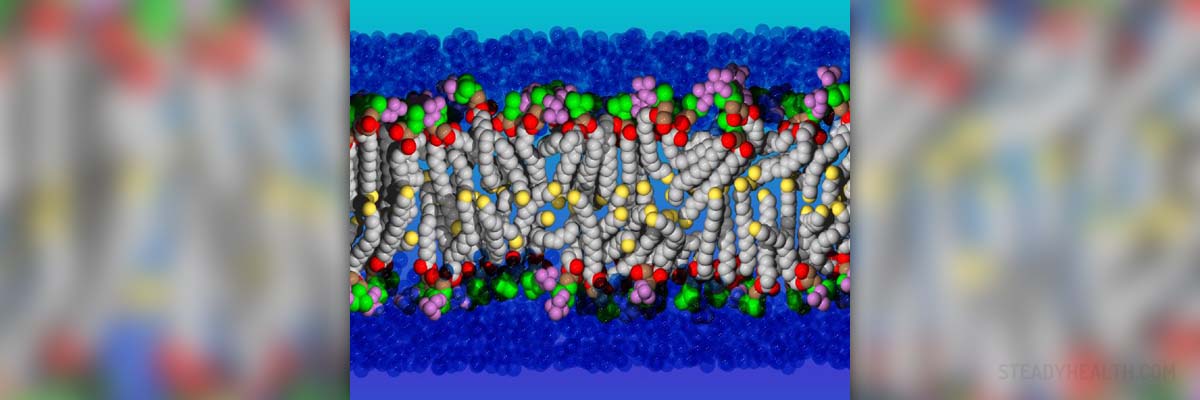
What are lipids?
Whatmost people think when someone mentions lipids is 'ugh, fat', but this is only partially true. Lipids are a group which encompasses three similar kinds of the chemical compounds - fats, waxes and sterols. And many of these are essential for proper functioning of the organism. Lipids are not soluble in water, are composed of carbon and hydrogen atoms, and play a pivotal role to the structure and function of cell membranes. Read on to see what this is all about.
Some generalknowledge
Human body obtains energy from oxidative breaking of compounds such as carbohydrates, fats and proteins. Fats are also used as long – term energy storage units. Fat deposits also serve as insulation, as they keep the body warm by preventing the body heat to escape and the cold to penetrate in the body (remember how marine animals in the arctic circle are fat). And stored fat is just a bunch of lipids stacked in fat cells.
Lipids are present not only in animals, but in plants as well. Oil that we get from various plants for, in example, use in our cuisine or in beauty care products is a lipid. Lipids are excellent for energy storage as they can store more energy per unit of mass than carbohydrates and proteins. Lipids can provide body with energy while there is little or no food available, provided that there is enough water available. You can live without food for days or weeks on end if you have sufficient fat reserves. In example, animals that hibernate in the winter or migrating birds, which fly hundreds and thousands of miles without eating survive solely on fat reserves.
Specificknowledge
As we mentioned, there are several groups of lipids. Triglycerides are compounds which are found in the cell cytoplasm and serve for energy storage. These are made when one molecule of a complex alcohol known as glycerol reacts with three molecules of fatty acids. Structure of a triglyceride resembles a trident, glycerol is its base while fatty acids its spikes. Difference in chemical structure determines whether triglycerides will stay liquid or solidify at 20ºC. Solid compounds are commonly called fats while liquid compounds are called oils.
Phospholipids are complex lipids, composed of molecules of different properties, so that one side of them is water - attracted while the other is water - repelling. This unique property of phospholipids makes them the chief building substance in cell walls.
Lipoproteins are molecules composed of lipids and proteins. Enzymes, antigens and structural proteins are lipoproteins. There are two kinds of them: HDL (High Density Lipoproteins) and LDL (Low Density Lipoproteins). Lipoproteins allow the water – repelling fat to travel in the water – rich blood.
Waxes are composed of fatty acids and long chain alcohols. Wax function is to form a protective semipermeable layer for the cells. They are found in both plants and animals.
















Your thoughts on this
Loading...