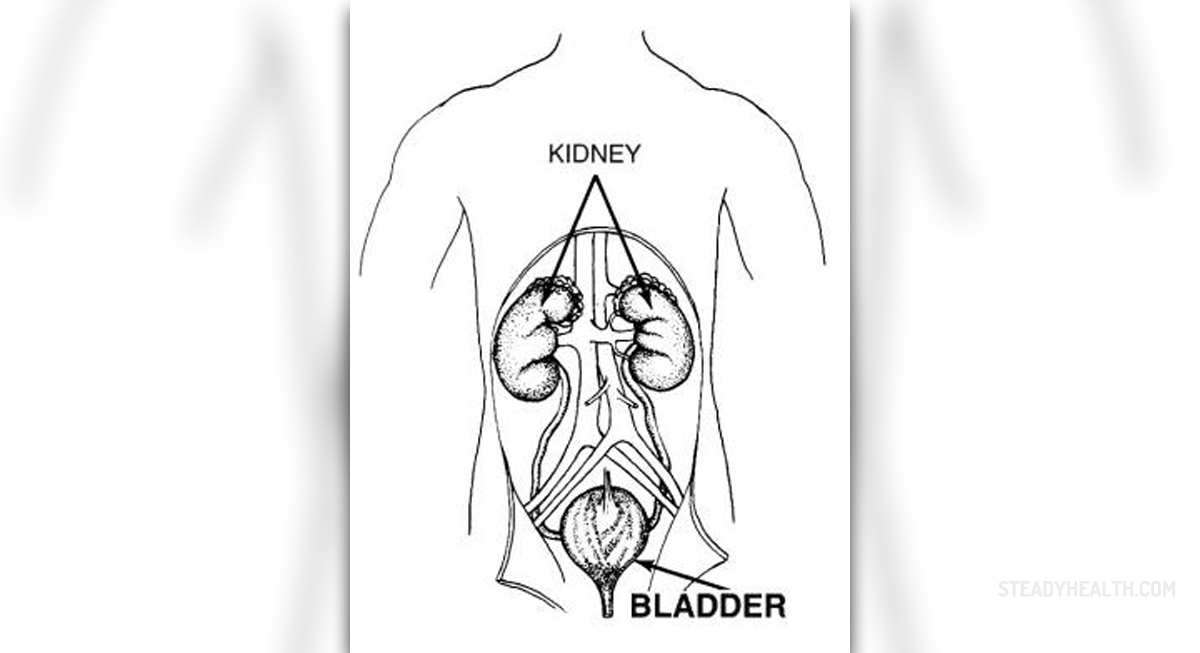
Bladder Cancer OverviewThe bladder is a hollow, balloon-shaped organ, positioned in the lower abdomen. Its function is to store urine and discharge urine through the urethra. Cancer of the bladder is a malignant tumor that develops in the bladder. This cancer usually forms in cells of the inner lining of the bladder. Bladder cancer is highly treatable if it is caught in the early stage.
In the U.S. cancer of the bladder kills over 12,000 people every year and more than 50,000 new cases of bladder cancer are diagnosed. This cancer is three times more common in men than in women. The highest incidence of bladder cancer is among Caucasians whilst the lowest is among the Asian population.
Causes and Risk FactorsScientists have still not explained what causes bladder cancer. However, there are several risk factors that are associated with this type of cancer. Cigarette smoking is considered to be the main risk factor for cancer of the bladder and people who smoke have two times more chance for developing bladder cancer comparing to non smokers.
Exposure to cancerous chemicals is also identified as the risk factor for bladder cancer. Family history of cancer of the bladder also increases the predisposition in a person. Medical history of urinary infections or kidney stones can lead to bladder cancer as well. Other risk factors for the cancer include gender (male), hormone replacement therapy, radiation therapy and chemotherapy as well as previous cancer of the bladder.
Signs and Symptoms of Bladder CancerCancer of the bladder is associated with several signs and symptoms. The initial symptom of the cancer is usually blood in the urine (hematuria). Urine may appear yellow-red or dark red. Pain and burning sensation while urinating as well as frequency of urination accompany bladder cancer too. Frequent urinating of small amounts of urine and frequent infections in the urinary tract are common too. Additionally, cancer of the bladder can be accompanied with the abdominal and lower back pain.
Diagnosis of Bladder CancerIn order to diagnose bladder cancer, a physician must perform a physical exam and evaluate the medical history of a patient. Next, the physician will order a urine test and urine culture to check for the presence of bacteria and cancerous cells.
Diagnosis of bladder cancer also includes a diagnostic test called cytoscopy. Cytoscopy involves the examination of the bladder with the help of a tube called cytoscope. During the cytoscopy, the doctor may perform the bladder biopsy.
In case the cytoscopy confirms the cancer, a chest x-rays are done to determine whether the cancer have spread to the lungs. CT and MRI scans can help to determine the metastasis to other organs.
Treatment for Bladder CancerTreatement for bladder cancer depends on the cancer stage, medical history and overall health of the patient. Surgical treatment for bladder cancer involves removal of the tumor and this treatment is usually used when the cancer is diagnosed in the early stage when it is still limited to the bladder.
Partial cytectomy and total cytectomy involve a partial or a total removal of the bladder and it is used when the cancer has spread. Radiation therapy and chemotherapy are also used to kill cancer cells and to fight the disease.












Your thoughts on this
Loading...