
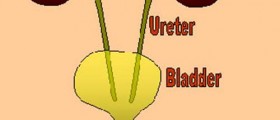
Hemorrhagic cystitis is an acute medical condition that leads to bleeding from the bladder due to diffuse inflammation of the organ. Patients suffering from hemorrhagic cystitis typically develop dysuria (painful urination), hematuria (presence of red blood cells in urine) and may sometimes experience spontaneous bleeding from the urinary tract.
This rather severe condition is a side effect of treatment with some medications such as cyclophosphamide, ifosfamide and may result from radiation therapy.
Acute Hemorrhagic Cystitis: Causes
As it has already been mentioned this medical condition is closely related to intake of certain drugs. Medications which are capable of causing hemorrhagic cystitis are usually chemotherapeutics. It is confirmed that hemorrhagic cystitis can affect individuals treated with cyclophosphamide and methotrexate.
Furthermore, the condition is also one of several side effects of radiation therapy. And finally, it may be associated with some infections. For example, in children acute hemorrhagic cystitis may occur after infection caused by Adenovirus (especially serotypes 11 and 21).
It is estimated that radiation therapy is less potent in causing hemorrhagic cystitis comparing to certain chemotherapeutics. One more important fact is that post-transplantation patients represent a risk group for this condition. They may easily develop hemorrhagic cystitis which is either connected to effects of chemotherapy or activation of dormant viruses in the kidneys, ureter and bladder due to immunosuppression.
Diagnosis and Treatment of Hemorrhagic Cystitis
A well experienced doctor can confirm hemorrhagic cystitis after performing a physical examination and investigating patient's medical history. In immunocompromised individuals the infective agents responsible for inflammation can be easily cultured.
Differential diagnosis includes numerous conditions some of which are UTI, kidney diseases such as kidney stones, inflammation of the prostate, endometriosis, cancer of the urinary tract etc. Still, if a person has recently been on chemotherapy or undergone radiation therapy these two may be most definitely taken as triggers of the condition.
Viral hemorrhagic cystitis in children is not so serious and resolves on its own within a few days.
Other patients require proper evaluation and adequate treatment. One of the first goals of treatment is connected with clot evacuation. Obstruction of the urinary tract with blood clots may consequently result in urosepsis, bladder rupture and renal failure. Clot can be removed with a wide-lumen bladder catheter and the bladder may be irrigated. Both of the procedures must be carefully performed since there is a risk of bladder perforation.
Hemorrhagic cystitis caused by cyclophosphamide may be prevented with aggressive hydration during the treatment. And finally, there is no effective treatment for hemorrhagic cystitis caused by radiation therapy.















Your thoughts on this
Loading...