Cancer Introduction
Cancer is a condition in which some previously normal cells go overboard and begin to multiply over and over again. They destroy the tissue from which they originated, consume nutrients that the healthy, normal cells need and create excess metabolic waste which acts as a poison for the organism. Cancer is a life-threatening condition for which there is no certain cure and success of treatment is heavily related to the early recognition of the problem and early start of thetreatment.
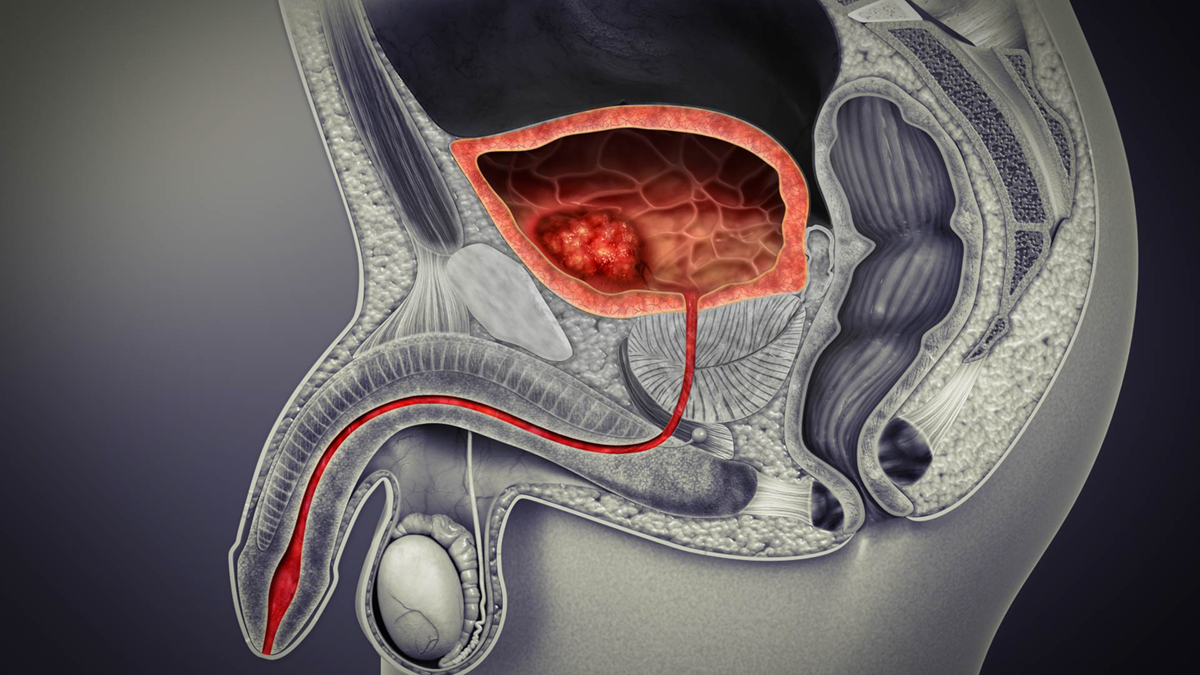
Bladder Structure and Types of Bladder Cancer
Bladder is a part of the urinary system, a hollow organ that is used as storage container for urine, from which the urine is excreted periodically. This is an evolutionary strategy of mammals, including humans. Bladder is made of a layer of muscles that encircles the wall of the bladder. This wall consists mostly of two kinds of cells, transitional and squamous, while, the third type of cells are cells that form glands that secrete bladder mucus. Cancer can develop in all these types of cells and is named accordingly - transitional cell carcinoma (by far the most common type of bladder cancer), squamous cell carcinoma, and adenocarcinoma, respectively.
Cancer Risk Factor
Why cancer develops is still unknown, but some factors that increase the risk of developing cancer are sex, as men are more prone to developing cancer, smoking habits, genetic predisposition, previous history of cancer, or exposure to some chemicals used in some branches of manufacturing industry.
Symptoms of Bladder Cancer
Bladdercancer has symptoms similar to some other diseases, such as infections or bladder stones. If it spreads to nearby organs it can provide additional symptoms. However, common symptoms are blood in the urine, urge to urinate and painful or burning urination, and pain in the abdomen or pelvic area. Advanced stages of cancer cause additional symptoms such as lack of appetite and weight loss for no apparent reason, fever, anemia, pain in the rectal and anal area or in bones. There is no difference in symptoms between children and adults.
Diagnosis
Cancerdiagnosis is complex and involves a thorough study of one's medical history and various tests and examinations and biopsy. Cancer may be treated with chemotherapy, radiation therapy, surgery and biological therapy (or immunotherapy). The good side of bladder cancer is that it is usually identified very early and can therefor be treated successfully. Unfortunately, it can reappear, so one with a history of bladder cancer must always be wary.













Your thoughts on this
Loading...