There are different types of ovarian cancers but the most common type is cancer of epithelial cells of ovaries. Women between 40 and 65 are at greatest risk of developing ovarian cancer, and according to the statistics, this is the seventh most common cancer among women in the United States (US).
The treatment often includes surgical removal of the cancerous tissue and chemotherapy. In some cases, chemotherapy (treatment with anti-cancer drugs) might be suggested by your doctor both before and after the surgery, or only after the surgical procedures. Certain types of ovarian cancer are not treated with medications after the surgical removal of the cancerous tissue.
Surgery for Ovarian Cancer
Surgical procedures used for ovarian cancers include the elimination of cancerous tissue. The gynecologist oncologist surgeons will try to remove as much cancerous tissue as they can, and these procedures are known as optimal cytoreduction or optimal surgical debulking.
Chemotherapy for Ovarian Cancer
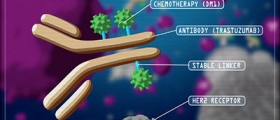
Chemotherapy is actually the treatment with certain drugs, in order to stop the growth of cancer cells in the body. Drugs affect the growth and reproduction of fast growing cells, which are cancer cells. Most of the normal human cells are growing slow and they are not affected by chemotherapy. However, there are also fast growing normal human cells – hair, gastrointestinal and bone marrow cells, which get affected with the use of anti-cancer medications. Effects on the normal cells caused therefore some unwanted side effects, such as the loss of hair, intestinal problems and blood-relatedproblems.
In general, chemotherapy medications can be given intravenously (IV), but there are some oral drugs, as well as some intraperitoneal (IP) drugs, given to the patients’ abdomen.
As mentioned, chemotherapy can be given before and/or after the surgical procedure. If it is used before the surgical removal of the ovarian cancer this type of therapy is known as neoadjuvant chemotherapy and after the surgery is adjuvant chemotherapy.
The most commonly used chemotherapy medications for ovarian cancer patients are Taxol (paclitaxel) and carboplatin and cisplatin (chemotherapeutic drugs made of platinum). Usually, doctors recommend taking the combination of paclitaxel and a platinum-type medication as the drugs of choice for patients suffering from ovarian cancer.
Treatment of Ovarian Cancer According to the Stage
The treatment for ovarian cancer depends on the stage of the cancer. If the woman’s cancer is in the stage IA or IB doctors usually won’t recommend any chemotherapy after the surgery.
Women with IC or other higher grade ovarian cancer could be advised to have adjuvant chemotherapy, usually a combination of paclitaxel and platinum-type medication. The treatment should start couple of weeks after the surgery and each cycle of medications should last for three weeks. The number of cycles of treatment may vary from 3 to 6, depending on the specialist. Another option for these women is the treatment with carboplatin alone, more often recommended in Europe than in the US.
Stage II patients are also advised to use adjuvant chemotherapy with the same drugs, and to use IP or IV chemotherapy after the surgical removal of the cancer.
Stage III and IV ovarian cancer patients should also use chemotherapy for 6 cycles. Some new researches suggest the use of another drug, known as bevacizumab (Avastin) as the additional treatment, along the combination of paclitaxel and platinum drug. IP chemotherapy is recommended for optimally removed cancer in stage III, but the toxicity and complications of the treatment might make it less acceptable than IV chemotherapy.










Your thoughts on this
Loading...