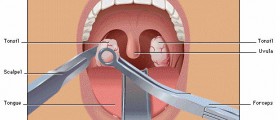
What is Throat Cancer?Throat cancer is a cancer that forms in the tissue of throat (pharynx), voice box (larynx) or tonsils. Pharynx is a 5 inch long hollow tube that starts behind the nose and ends at the top of esophagus. The pharynx is divided into three segments: the upper part of the throat behind the nose (nasopharynx), the middle part of the throat behind the mouth (oropharynx) and the lower part of the throat (laryngopharynx). Throat cancer can refer to any of these segments and can be identified as nasopharyngeal cancer, oropharyngeal cancer, or hypopharyngeal cancer.
Causes of Throat Cancer
Throat cancer occurs when malignant tumor develops in the mucous membrane lining the throat. Such tumor forms when cells of the throat start to abnormally grow or multiply uncontrollably. As it was mentioned earlier, throat cancer is commonly associated with the use of tobacco and excessive alcohol drinking. There are other factors that may increase the risk of throat cancer. They include poor oral hygiene and poor diet that lacks vitamins and minerals and includes plenty of salty meat. Prolonged exposure to asbestos fibers that can be easily inhaled also increases the risk of throat cancer. Human papilloma virus (HPV) is associated with cancer of the throat too. People over 60 years of age are at high risk and throat cancer rarely occurs before the age of 50. Also, throat cancer is three times more common in man than in women.
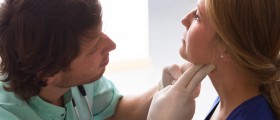
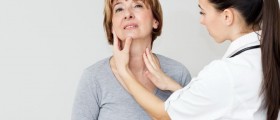
Symptoms of Throat CancerPerson affected by throat cancer may experience pain in throat and difficulty swallowing. Breathing can also become difficult. Hoarse voice and persistent sore throat can be present. Swollen lymph glands and lump in the throat are common symptoms of throat cancer.








-Disease-Cause-Oral-Cancer_f_280x120.jpg)


Your thoughts on this
Loading...