
Background
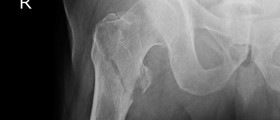
There is no one same fracture of the femoral shaft and there are plenty of different types of these fractures. A femoral shaft fracture can be anything from nondisplaced femoral stress fracture to a fracture associated with severe comminution and enormous soft-tissue injury. In case of these fractures, they are usually caused due to high-energy forces. These fractures are in most cases associated with multisystem trauma as well. People should also know that isolated injuries are also possible. These occur in cases when repetitive stress is present and may be seen when there are also metabolic bone diseases, metastatic disease or primary bone tumors. In most cases of these fractures, people need to know that the most common way of treatment is surgery. In this surgical procedure, plate fixation or intramedullary nails are also present. The goal of these surgeries is to establish anatomic stabilization and allow mobilization as soon as it can be allowed. Surgical stabilization is important for another reason as well and that is early extremity function. This is important for both the knee and the hip, in order for them to be allowed both motion and strengthening. A person may suffer from long-term effects on the knee and hip if alignment is not properly restored. People need to know that the treatment of these fractures has improved tremendously during the last 100 years. Before the modern methods, the only way of treatment was either traction or splinting. It was not uncommon for these fractures to be fatal. People need to know that the femur is highly vascular and fractures are highly likely to end up in loss of a lot of blood in the thigh. Almost half of all the isolated fractures require transfusion.
Rehabilitation programPhysical therapy
A person will not perform the treatment plan on his or her own. It will be performed by an orthopedic and in most cases a surgical stabilization is involved. At first, people will perform touch-down weight bearing. Once there is no more pain, the patients will move on to full weight bearing. Running needs to be avoided in the first 8 to 16 weeks. However, the patient will be able to cycle, swim and run in chest-deep water.
Complications
The alignment needs to be restored when these fractures are considered. In case of limb deformity, certain precautions are applied, in most cases a splint.
Surgical intervention
In case the fracture is a special one, the surgeon will consult a certain specialist. Before surgery can be performed, the patient needs to be hemodynamically stable. Definitive surgical stabilization usually lasts for 24 hours.











Your thoughts on this
Loading...