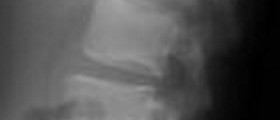
The femur is the biggest and most powerful bone in our body. It requires the application of a significant amount of force in order to fracture the femur. With regard to risks and complications of the injury, bleeding can be intense as a result of rich blood supply to the area, and, further to this, open fractures or wounds can lead to infection. There are three types of fracture that can occur: spiral or transverse (I), Comminuted (II) and open (III).
Symptoms
Normally, femoral fractures occur when significant force is applied to the area. Fractures can lead to severe pain and even physical deformity. During diagnosis, it is necessary to rule out the possibility of an associated injury having occurred, for example, hip fracture or knee ligament injuries. The affected extremity might appear shortened, and crepitus might be visible during movement. The thigh might appear swollen as a result of bruising, while visible deformity and tenderness will be observed at the site of the injury.
Injury might also cause some damage to related arteries. Some symptoms of this include hematoma, lowered pulse rate, significant blood loss, tachycardia and hypotension. Nerve injury is normally not seen with this type of injury, but some neurologic difficulties can arise due to resultant trauma, cysts, lytic lesions, cancerous metastasis, Paget disease or bone cysts.
Treatment
Before arrival at the hospital, the leg should be splinted as soon as possible. If open fractures occur, sterile bandages should be applied. Should the wound be badly contaminated, sterile saline irrigation can be used to rid the wound of major contaminants.
When the patient reaches hospital, in-line traction should be used to realign the fracture. This can help with pain relief and can reduce bruising. A pneumatic splint might also be used to reduce blood loss and bruising. As regards pain, opiate-type analgesics are used to combat the severe pain that is likely to be experienced. Intravenous administration of the opiates is the most efficient method of pain relief. Tetanus toxoids and antibiotics must be used to combat infection in the case of an open fracture. Cephalosporin is normally used for this, in combination with gentamicin. If a patient has suffered significant blood loss, then he or she might require resuscitation through the use of crystalloids. A nil-by-mouth order should be passed until the patient has seen an orthopedic surgeon.
In the course of treatment for a fractured femur, it will most likely be necessary to consult with an orthopedic surgeon; additionally, one might require the consultation of a vascular surgeon in the case of neurologic compromise.









Your thoughts on this
Loading...