
Borderline personality disorder is a serious mental illness distinguished by extreme emotional instability. Patients with borderline personality disorder usually have recognizable patterns of emotional unsteadiness, serious difficulties in interpersonal connections and impulse management. These people normally have disturbed cognitive processes and the illness often disrupts their whole family and social life, as well as the sense of self-identity. It is estimated that borderline personality disorder affects approximately 2% of adult population, mostly young women.
Signs and symptoms of borderline personality disorder
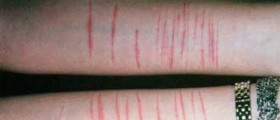
Borderline personality disorder manifests trough unusual levels of mood instability. Person may sometimes feel like split person or may rapidly swing from black to white thinking. Person with borderline personality disorder will alternately idealize and demonize the others, which may eventually weaken and destroy social relationships with family, friends and co-workers. It is not unusual for these people to rapidly change their self-image or develop love-hate relationships with others. A high rate of self-injury without suicide intent, is associated with bipolar disorder, as well as a significant rate of suicide attempts and completed suicide in severe cases.
The most common symptoms of borderline personality disorder include: impulsive behavior associated with high risk, risky driving, unsafe sex, or drug abuse; extremely strong but fluctuating emotions; short but highly intense episodes of nervousness and depression; groundless anger that escalates to aggression, or even a physical confrontation; difficulty to control emotions and impulses; suicidal behavior; fear of being alone.
Causes of borderline personality disorder
The true causes of borderline personality disorder are not yet fully understood. However, doctors have determined a number of factors that may be associated with the development of this illness. Borderline personality disorder may be genetically inherited, as some of the clinical studies involving twins and families suggest. Environmental factors are also important as many people diagnosed with borderline personality disorder have a history of childhood abuse, abandonment and partition from care-givers or their loved ones. Certain studies reveal the connection between brain abnormalities and borderline personality disorder. According to these studies, problems in particular areas in the brain, responsible for emotional management, impulsiveness, and anger may cause this mental illness.
Treatment of borderline personality disorder
The diagnosis should not discourage people with borderline personality disorder. The treatment of borderline personality disorder has significantly improved in recent years. Dialectical behavior therapy is one of the examples. It is a psychosocial treatment developed specially to treat borderline personality disorder. Treatment may also include prescribed medication such as antidepressant drugs and mood stabilizers.
















Your thoughts on this
Loading...