Development
The causes of the condition are varied - there is no defining cause of BPD. Psychological, social or even biological problems can all cause or combine to cause the onset of BPD. It is suggested that low serotonin levels in the brain can lead to impulsive tendencies - impulsion and emotional instability can be hereditary. On the psychological side of things, BPD may be caused by the memory of a traumatic childhood or even a single traumatic event. Environmental factors, such as the impersonality of modern society or a struggle for identity can lead to development of BPD. It is likely that BPD will be caused by a combination of several different problems - perhaps a neglected childhood, perhaps domestic abuse or similar tragic occurrences. The cause will vary in each patient.
BPD usually firsts manifests during adolescence. Approximately eighty percent of sufferers are women. Problems normally remain present for a long period of time, with about ten percent of cases resulting in suicide. However, the condition does tend to lessen by the time middle age descends - the reason for this is not yet known. Some BPD patients are capable of functioning fully - they might develop a successful career, lead a happy family life, etc., and for most, the disease will eventually become more manageable over time.Treatment
Sometimes drugs are used to treat BPD. This approach generally only serves to reduce negative symptoms. For this reason, the main treatment used to combat BPD is psychotherapy. Psychotherapy usually results in gradual improvement in the patient. Therapists will usually try to build a relationship of trust with the patient, thus providing something of a haven for the patient. The therapy will be mostly aimed at reducing impulsive tendencies, as this can help patients’ judgment to improve.
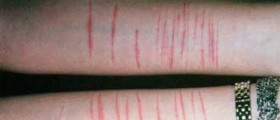
If memories of traumatic events are causing the BPD, then the therapist might look to examine and uncover these events or experiences. However, some feel that uncovering these events merely serves to make the patients feel worse. Cognitive behavioral therapy can be useful for BPD patients, and it has been shown to reduce suicidal tendencies in many patients.







-Causes,-Symptoms,-Diagnosis-And-Treatment_f_280x120.jpg)








Your thoughts on this
Loading...