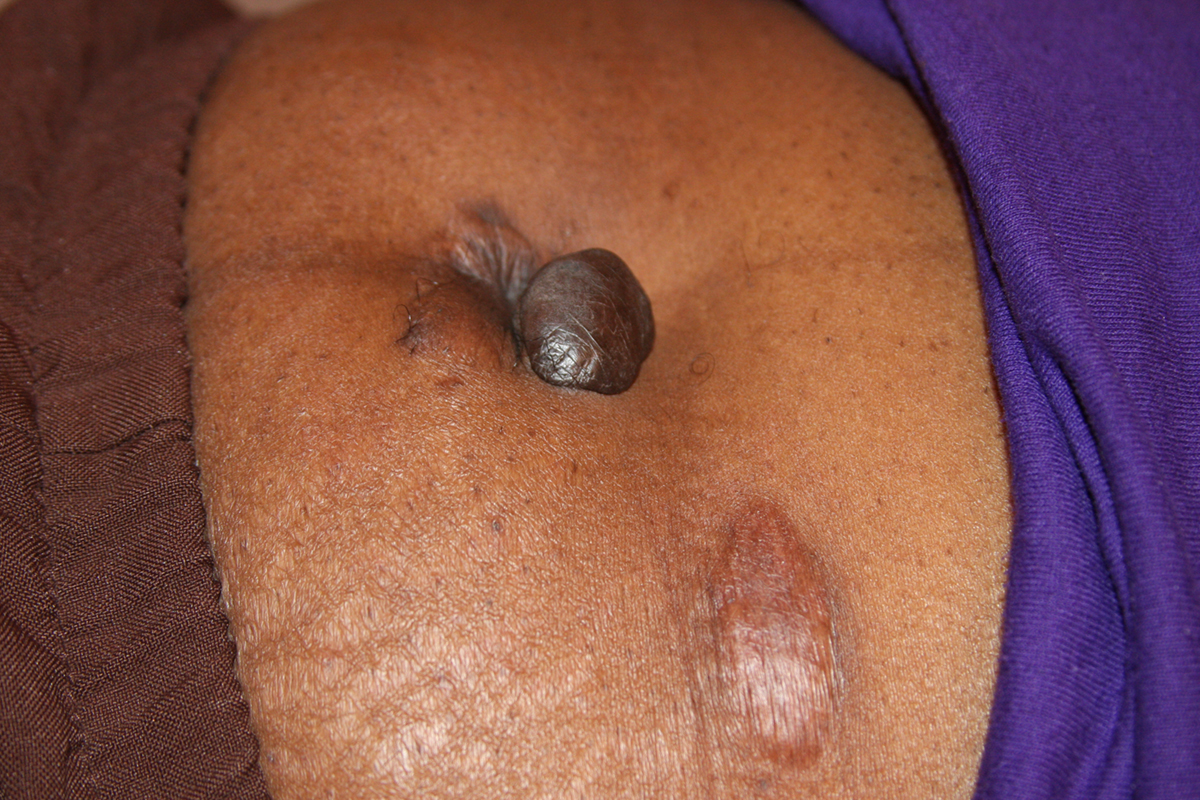
Keloids are actually hypertrophic scars. They represent extreme growth of scar tissue. Keloids can develop after injuries or after surgical procedures. These skin changes predominantly affect dark-skinned people and only sporadically occur in fair-skinned people.
Keloids are not tumors. Still in many people keloids are aesthetic issue since the overgrowth of the skin tissue may be so intensive that it can change normal appearance of the skin. The scars are usually at the same level of the skin. Keloids grow above this level and even when they are surgically removed they tend to reoccur.
Causes of Keloids
The most common causes of keloids include increased level of melanocyte hormone, insufficient amount of fully developed collagen and high amount of soluble collagen.
Any trauma that affects skin and leads to its tear can cause keloid formation in susceptible people. This even refers to slightest skin injuries such as vaccination. Dark skinned people are predominantly affected by keloids.
Even genetics can play significant role in getting keloids. It is known that one can be affected with these skin changes, if someone else from the family suffered from keloids.
Some believe that prolonged exposure to the sun can eventually result in keloids.
Even in people who are not prone to keloids they can develop in case that the wound that is under process of healing gets infected or is under tension.
And finally, people between 10 and 30 years of age are predominantly affected by these skin changes.
Symptoms of Keloids
The most obvious sign of keloids is excessive formation of the scars. The scar tissue spreads in all three directions and affects larger portions of the skin comparing to the initial injury or surgical incision. The color of keloids is darker and redder comparing to ripe scars. In rather rare cases keloids may induce pain or irritation.
Elevated scars that are hard to touch are most likely keloids. The affected person may even notice the growth of the keloid and report it to the doctor.
Treatment of Keloids
Keloids are very difficult to get rid of. There are several treatment modalities available including skin grafts, excision of keloids or laser surgery. In some patients the growth of the keloids can be stopped by injections of corticosteroids. Laser surgery can be effective in elimination of redness of the affected skin but can do much regarding the size of the keloid. In some cases cryosurgery may be effective.
Silicone sheeting is a method in which a silicone sheet is applied onto the keloid over the night for more than a few months. In that period of time keloids may reduce in size. Even prolonged compression with bandages can lead to certain positive results. And the most extreme treatment modality includes radiotherapy in which the area of the scar is exposed to ionizing radiation which will consequently result in smaller scar. The only thing is that radiotherapy must be applied during the healing process and scar formation.
Unfortunately, none of the previously mentioned treatment modalities provides with suitable result and the patient can only expect slight reduction in size of keloids instead of their complete elimination.
















Your thoughts on this
Loading...