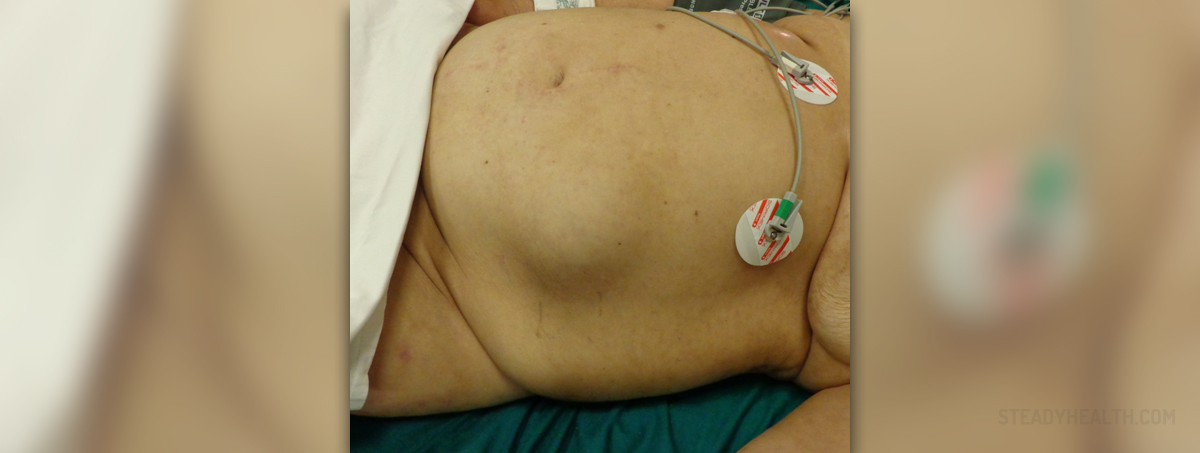
Hernia
Muscles in the human abdomen serve, among the other things, to hold abdominal organs in place. If, for some reason, they weaken on some spot, a part of abdominal tissue or a loop of intestine can push through the muscles and end immediately under the skin. This is known as hernia. A special type of hernia is ventral, or incisional hernia. This type of hernia is linked to surgery, as it happens on location of a surgical scar. It is known that up to thirty percent of patients who have undergone surgery in the abdominal region may develop ventral hernia. On the other hand, umbilical hernia occurs at the navel (the belly button) and need not be related to previous surgical procedure.
Symptomsof ventral hernia
In some cases, the affected person does not feel any kind of hernia – related discomfort and the only symptom that something has happened is the appearance of the bulge under the skin in the scar region. Pain related to ventral hernia can be felt when the affected person is trying to lift heavy objects, coughing, straining while passing stool or urinating, or standing or sitting for a long time. These and similar activities exert pressure on the abdomen and cause pain in the region.
A more serious condition related to ventral hernia is strangulation. This happens when the loop of intestine that has herniated becomes tightly trapped (strangulated) in the ruptured layer of muscle. This cuts off the blood supply to that part of the intestine and leads to severe abdominal pain, nausea and vomiting. The strangulated part of the intestine can die off, or there might be more serious problems. Strangulation is therefor regarded as medical emergency, a situation which requires immediate doctor's attention.
Causes of ventral hernia
Abdominal muscles become weakened after the abdominal surgery if the incision goes through them. Intestine or abdominal tissue can herniate through this weakened section of the abdominal muscles if the person in question lifts heavy objects, coughs continuously, strains when passing stool or urinating, or suffers from severe vomiting. Conditions that increase risk of ventral hernia include being overweight, pregnancy, diabetes, or use of steroids. Also, postoperative complications such as infection of the incision increase the risk of developing ventral hernia.
Diagnosis and treatment.
Typically, it suffices to cough. The doctor will be inspecting region of suspected herniation while you cough, as the hernia will expand at that moment. In some cases, exact diagnosis will require use of computer tomography. Treatment is surgical. If possible, doctors will be using the minimally invasive laparascopic methods to repair the hernia. Still, some cases of hernia cannot be treated with minimally-invasive techniques and such patients will have to undergo open surgery. Type of surgery will be chosen after a detailed examination.











Your thoughts on this
Loading...