The Causes and Symptoms of Hiatal Hernia
Hiatal hernia is a condition in which the stomach bulges into the chest cavity, mostly due to the weakened or defective muscle, which is called the diaphragm and which has the purpose of dividing the chest from the abdomen. This happens when there is some kind of an injury to the stomach area or when the surrounding muscles are under constant and intense pressure due to lifting heavy things, or due to coughing, vomiting, or other straining activities. Some people are born with certain defects or abnormalities of hiatus, which also results in hiatus hernia.
Hiatal hernia can be either small or large, and if it is small, it usually does not cause problems to people, so they are often unaware of having it. However, a large hiatal hernia causes serious problems related to nausea, heartburn, belching, and even pain in the chest. If any of these symptoms are persistent, the person should schedule an appointment with the doctor.
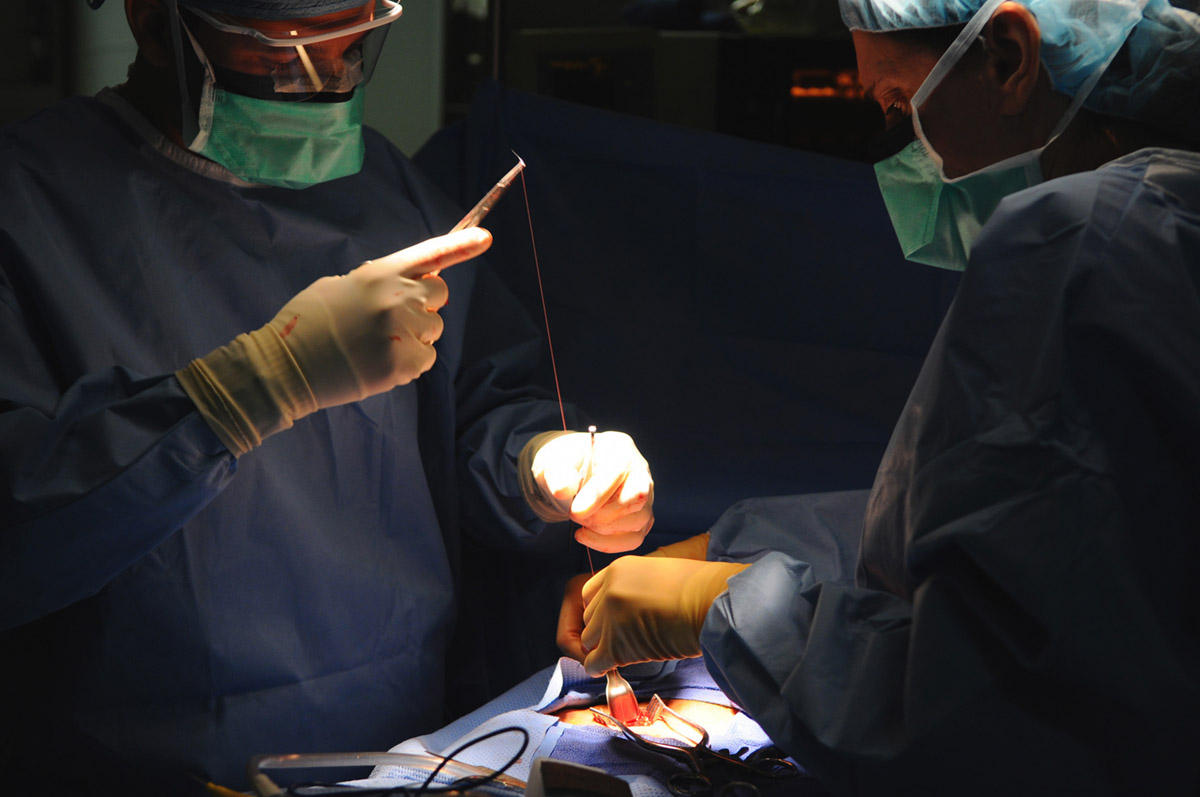
Surgery for Hiatal Hernia
The treatment of hiatal hernia is required only in cases in which this condition causes certain problems and symptoms. The available methods include medications or surgery, but the fact is that surgery is done very rarely, usually only in cases of emergency, or in cases in which the treatment with medications or change in diet did not give any positive results.
This kind of surgery is done under general anesthesia, and depending on the case and type of the procedure, it may require one or two incisions, one for the surgery instruments, and another for the insertion of a laparoscope, if necessary. During the surgery, in cases of the defect in the diaphragm, the stomach may need to be pulled out into the abdominal cavity, and the upper part of the stomach needs to be wrapped around the esophagus; in cases of a weakened esophageal sphincter, it is necessary to reconstruct it, while other cases simply require the removal of the hernia sac.
Depending on the case, the surgery for a hiatal hernia can be done on an inpatient or outpatient basis, which means that the patient may go home the same day or may be required to stay in the hospital for a few days after the surgery. However, the recovery period takes approximately two to four weeks, after which the patient can go back to everyday activities and normal life.
- The incidence of symptomatic cases of hiatal hernia appears to be linked to the diagnosis of gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD), the 2 conditions being closely associated. The most characteristic manifestation one will find in hiatal hernia is gastroesophageal reflux, manifested through regurgitation and heartburn, while less common symptoms include dysphagia, epigastric or chest pain and even chronic iron deficiency anemia. Large hernias can present with dysphagia, early satiety or regurgitation.
- According to the Society of American Gastrointestinal and Endoscopic Surgeons, only investigations that will have an impact on the clinical management of the patient should be performed. The diagnosis of hiatal hernia can be rather challenging at times due to the shift in the anatomy of the esophagogastric junction during deglutition, respiration and movement. A complete history and physical exam is mandatory, as they may reveal symptoms that were not previously apparent.
- The PubMed database was screened for publications using the terms: “hiatal hernia”, “paraesophageal hernia”, “management”, “treatment”, “hiatal repair”. A literature review of contemporary and latest studies was completed. The studies that we looked into include prospective, randomized trials, systematic reviews, clinical reviews and original articles. The information was compiled in narrative review format.
- This narrative review presents new data on the diagnosis and management of hiatal hernia. While the diagnostic pathway has remained virtually unchanged, new data have come to light regarding the surgical treatment of hiatal hernia. We present the imaging methods used for its diagnosis, as well as the medical and surgical treatment currently available.
- medlineplus.gov/ency/article/002925.htm
- medlineplus.gov/ency/presentations/100028_2.htm
- Photo courtesy of Wikimedia Commons













Your thoughts on this
Loading...