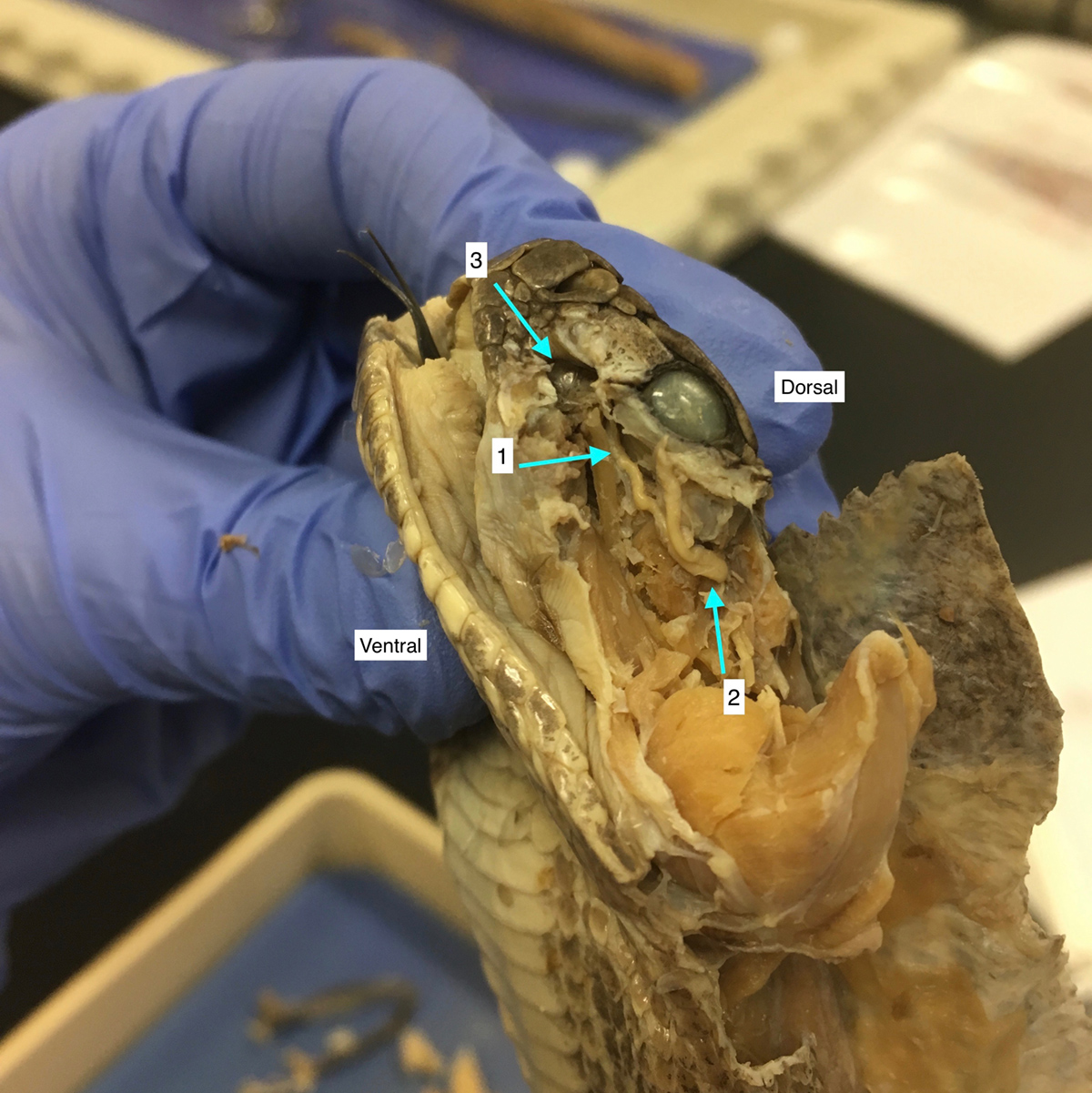
Trigeminal Neuralgia Overview
Trigeminal neuralgia is a neuropathic disorder and it features with severe facial pain. One or both trigeminal nerves can be affected. The pain can be present in all parts of the face as well as in the ears, scalp, teeth and jaw. The problem of trigeminal neuralgia is that it is hard to be treated, especially cured.
Patients describe the pain as stabbing and it occurs spontaneously. The disease can be triggered by cold weather, high pitches sounds, chewing and so on. The pain can last from few seconds to even several hours. This pain interferes in patients' lives and can ruin them. In time patients complain about more frequent attacks and even more intensive pain. A variant of this medical condition called atypical trigeminal neuralgia features with severe pain which resembles migraine. This pain accompanies already existing stabbing pain.
Causes of Trigeminal Neuralgia
The actual cause of trigeminal neuralgia is not known. Some believe that compression of the nerve leads to painful sensations. On the other hand, benign and malign tumors can also compress or infiltrate the nerve and induce pain.
This disease can additionally develop in patients who are already suffering from multiple sclerosis. Furthermore it can also occur connected to herpes simplex virus. In case that the actual cause cannot be fount trigeminal neuropathia is classified as idiopathic.
Surgery for Trigeminal Neuropathia
Surgical procedure is performed to relieve the pressure on the nerve. In well experienced surgeons 90% of all operated patients report pain relief.
Microvascular decompression is commonly performed in patients suffering from trigeminal neuralgia. The surgeon enters the skull through a hole behind the ear. The surrounding of the nerve is investigated to find the presence of a blood vessel which may have been involved in compression. After this blood vessel has been identified the surgeon separates the nerve and the blood vessel with a small pad. This procedure is rather successful and provides with chronic pain relief.
There are several more surgical procedures in which the surgeon uses needles or catheters to reach the point where nerve splits into three divisions. Percutaneous balloon compression is an excellent option for patients suffering from ophthalmic pain as well as those who still have to deal with pain even though they have already undergone microvascular decompression.
In some patients, the pain can be eliminated by glycerol injections and radiofrequency rhizotomies. Glycerol injections partially damage trigeminal nerve and this way the pain can be reduced. In radiofrequency rhizotomy the surgeon applies heat onto the selected portion of the nerve.











Your thoughts on this
Loading...