Trigeminal Neuralgia (TN) is also referred to as tic douloureux. It is a painful syndrome that usually appears on one side of the face.
Findings of a physical examination of someone suffering from trigeminal neuralgia are usually normal, other than some pin perception loss. This is why high-resolution neuroimaging should be used, in order to rule out other causes of the pain.
The way in which the pain appears is still not definitely determined. There are several theories. According to one, prior damage of trigeminal nerve causes the disturbance in ephaptic transmission between axons. Perhaps even central inhibitory mechanisms may be disturbed in some way.
Roots of the trigeminal nerve could also be irritated by numerous factors like cross compression of blood vessel nerve, tumors, aneurysms, and meningeal inflammations. Regardless of the cause, it is important to know that if person under 45 years of age starts developing trigeminal neuralgia, a possible development of multiple sclerosis should be taken into consideration. A lesion inside the central nervous system may be the cause of problems that are similar to trigeminal neuralgia, which appears due to the problems of the peripheral nervous system.
Pain reduction is the aim of pharmacologic therapy. There are several possible medical treatments like Carbamazepine (Tegretol), Gabapentin (Neurontin), Phenytoin (Dilantin), Trileptol, Klonazepin and Baclofen.
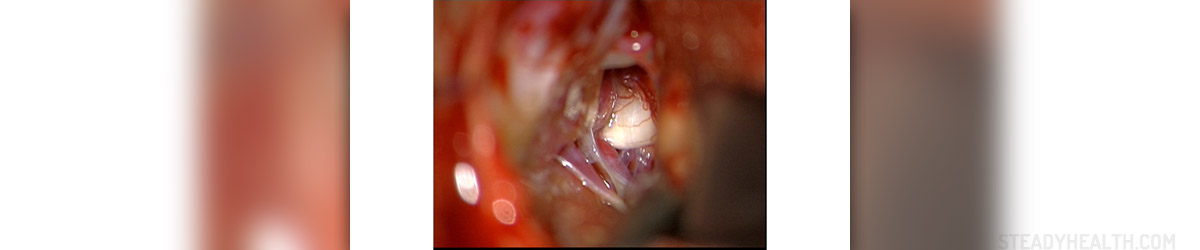
Before any kind of surgical intervention, an MRI needs to be taken in order to rule out other possible reasons of compression, like muscular malformations, large ectatic vessels, or mass lesions. Possible surgical interventions used for trigeminal neuralgia are blocks of peripheral nerves, needle procedures and craniotomy, which are followed by MVD (microvascular decompression) and stereotactic radiosurgery (Gamma Knife®).
Some percutaneous transovale needle techniques are balloon microcompression, glycerol rhizotomy, and radiofrequency trigeminal electrocoagulation. Microvascular decompression (MVD) is usually used with the younger patients. Elderly patients, patients with impaired hearing, recurrent pain after MVD, or with multiple sclerosis, are usually treated by Percutaneous techniques.
MVD generally offers the longest pain relief and, at the same time, preserves facial sensations.
Trigeminal Neuralgia Radiosurgery involves multiple beams of ionizing radiation which are being targeted at a certain point inside of the brain. A high dose of radiation is being used in a single session.
Radiosugery is considered to be good in the treatment of high-risk medical illness, patients with co-morbidities and pain refractory of previous surgeries. The reason for this is that it is the least invasive procedure in treatment of trigeminal neuralgia.
A possible complication may occur concerning facial numbness and increased facial paresthesia in a period of six months, or more.
A lower radiation dose is used for a repeated procedure, which is required in cases where patients are experiencing long-term recurrent pain.














Your thoughts on this
Loading...