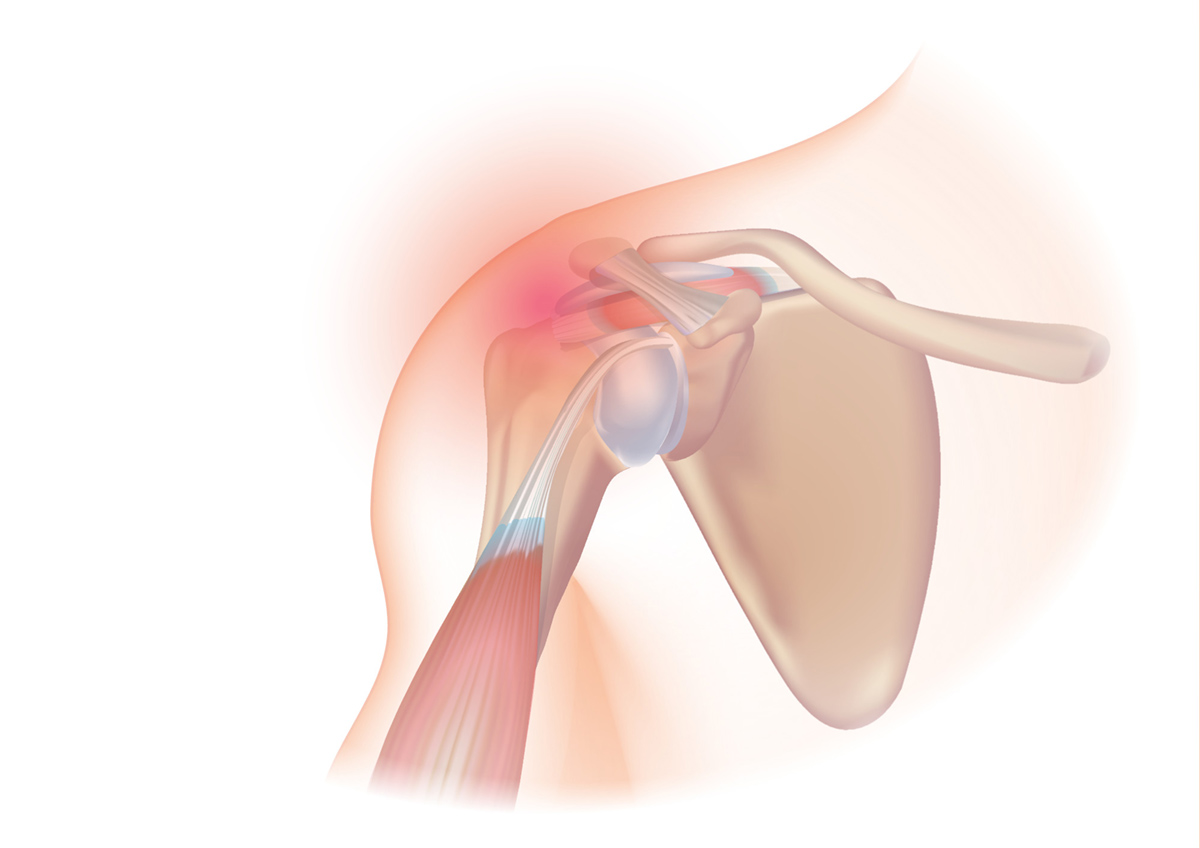
What is the rotator cuff?
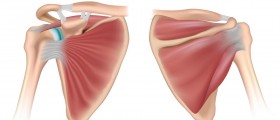
The rotator cuff is a common name for a group of four muscles in the human shoulder that are located around the shoulder joint and are responsible for moving the bone in the upper arm (and thus the arm) forward, back, and up. Two muscles are used to pull the hand up, while one muscle pulls it forwards and one pulls it back. Excess force may cause the tendon of some of those muscles to tear. It might be just a small crack, or the muscle may be completely detached from the (upper arm) bone, when we say that the rotator cuff is torn. this is a common sports injury, but anyone can be affected. It's enough to overburden the rotator cuff suddenly. If the tendon has been torn, it cannot heal (reattach to the bone) by itself and surgery will be required to fix this. There are four commonly used procedures for torn rotator cuff surgery. It takes up to two hours in most cases.
General settings
To allow for a comfortable operating position, the patient is half-seated and his head is supported. Operation are typically done under general anesthesia, meaning that the patient is asleep, but some surgeons use regional anesthesia (this kills off sensation of pain just in the targeted region, in this case, the shoulder that is being operated on) aided by a sedative, which helps to keep the patient aware, but calm and relaxed (a hard thing to do without aid while someone is putting sharp things in your flesh). The ultimate goal of every surgery is to reattach the torn tendon to the bone.
Surgery methods
Surgery is mostly based on making an incision through the deltoid muscle to get to the inside of the damaged rotator cuff, then removes the scar tissue that formed on the detached tendon, drills small holes through the upper arm bone and sews the tendon to the bone through these holes.
Impingement surgery is used to allow the rotator cuff to move freely if the space between the upper arm and a certain part of the shoulder blade (acromion) is too narrow and both hampers its movement and damages it. A small portion of bone from the underside of the acromion is cleaved away. This allows the tendons of the rotator cuff more space for movement and prevents their injury. Eventual bone spurs and swollen or irritated bursa (pouches filled with fluid that lie between the tendon and the bone) are drained or removed. This type of surgery is used to fix chronic tendinitis that does not respond to conservative (nonsurgical) treatment and is a common part of other rotator cuff surgical procedures.
Other common procedure is arthroscopic surgery. It is a minimally invasive technique, as the surgery is done through miniature incisure, usually the size of a button hole, through which all the instruments (tiny, designed for this purpose) and the operating field is viewed with a tiny camera. This type of surgery allows for a faster healing of the areas that need to be cut to get to the tendon (tendon still heals slowly) and less related risks. Still, as this procedure is complicated, open surgery is still common as it allows for a better view, and thus better control.










Your thoughts on this
Loading...