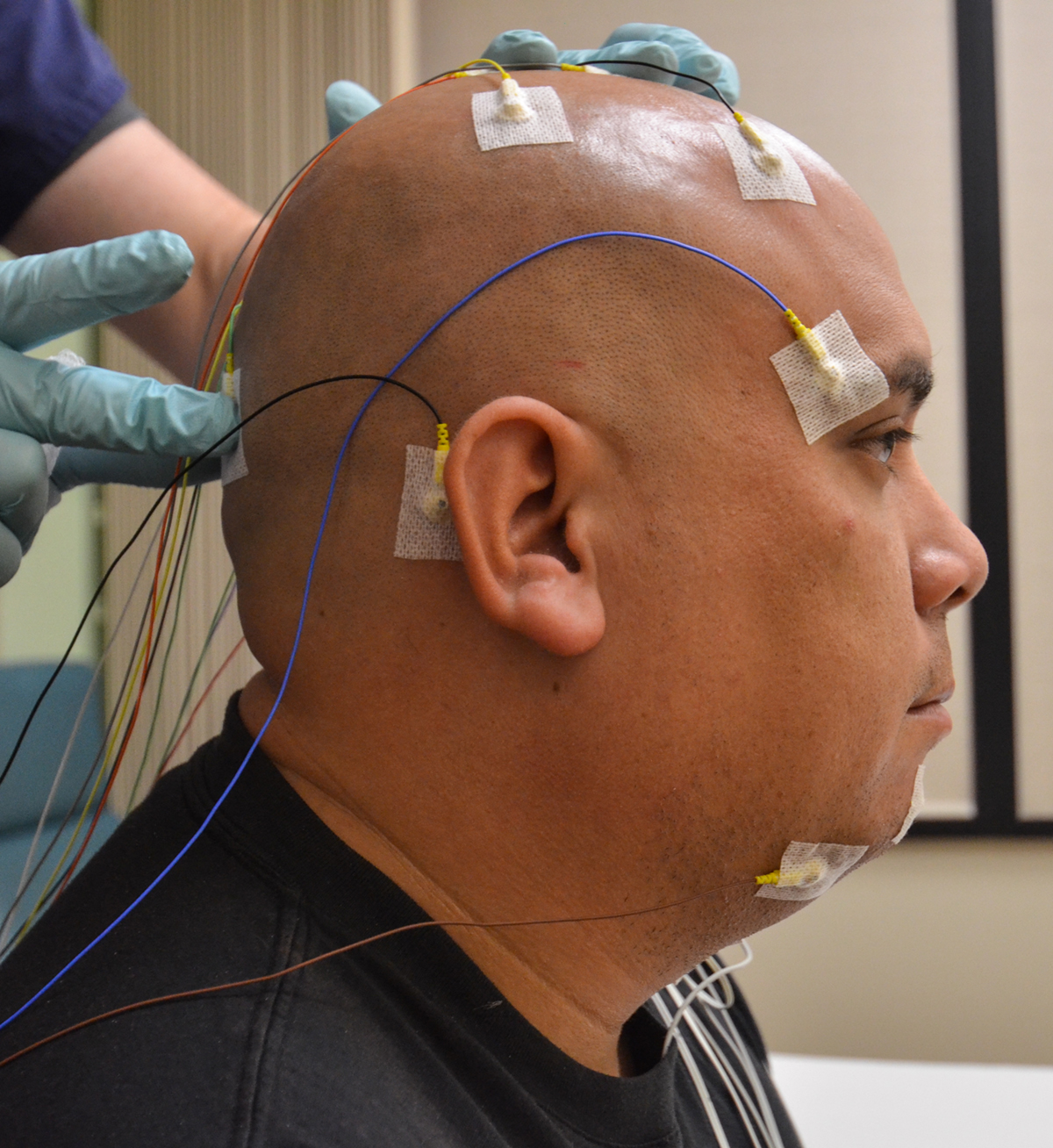
Obstructive sleep apnea
This condition can be life threatening and it has shown to produce morbid consequences for the body, such as obesity, hypertension, heart attack, stroke, diabetes, depression, dementia and even sudden death.
Some of the biggest health problems that a person can be riddled with can result from a case of sleep loss or sleep depravation.
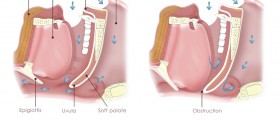
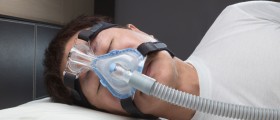
Obstructive sleep apnea (OSA) results from airway obstructions during sleep. A patient with OSA will either have a smaller airway or an unsteady airway with more chances that it will collapse.
The airway itself is made up of the upper and lower jaws, tongue, tonsils, soft palate, and the side walls of the throat.
Since the airway patterns and the severity of the obstruction can vary greatly from individual to individual, the surgical procedures for treating this problem are all very individual.
Also, the success rate of the surgery will vary as well, as will the general invasiveness of the surgery.
Not only is it dangerous for adults, but sleep apnea also affects 10 percent of children as well.
Some of the main symptoms of this condition include restless sleep, sweating during sleep, snoring, night terror, sleepwalking, bed-wetting, and daytime fatigue.
Usually, the symptoms are not as glaring in children. Adults tend to stop breathing because of the condition, which is very dangerous, and the snoring will be a lot louder and more noticeable in adults.
It is also important to note that it can be a familial problem, especially with siblings.
Treatments
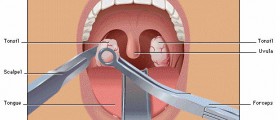
The most common treatments for OSA are the adenoidectomy and tonsillectomy.
Sometimes, turbinate reduction by radiofrequency can be performed in children along with the primary treatment.
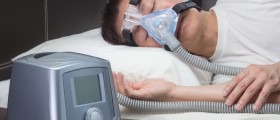
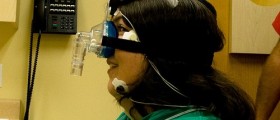
There must be a sleep study done before the surgery is scheduled in order to confirm the OSA and the extent of the problem, so that the surgery can be tailored to the individual’s problems and needs.
The success rate is very high, up to 80 percent, though sometimes, additional treatments are needed, such as orthodontic therapy for widening the jaw.
Adenoidectomy and tonsillectomy are very common operations. Sometimes, it is recommended to stitch up the wounds that were left from a tonsillectomy in order to improve the airway by wound closure, reduce the pain after the surgery, and reduce the risk of bleeding in the surgery.
The procedure will last about an hour and is performed under general anesthesia. There will be pain and a swelling of the throat after the operation, which means that the food intake will also be decreased for the time being. There is also a chance of bleeding, though it is not very common, since only about two percent of patients experience post-operative bleeding.










Your thoughts on this
Loading...