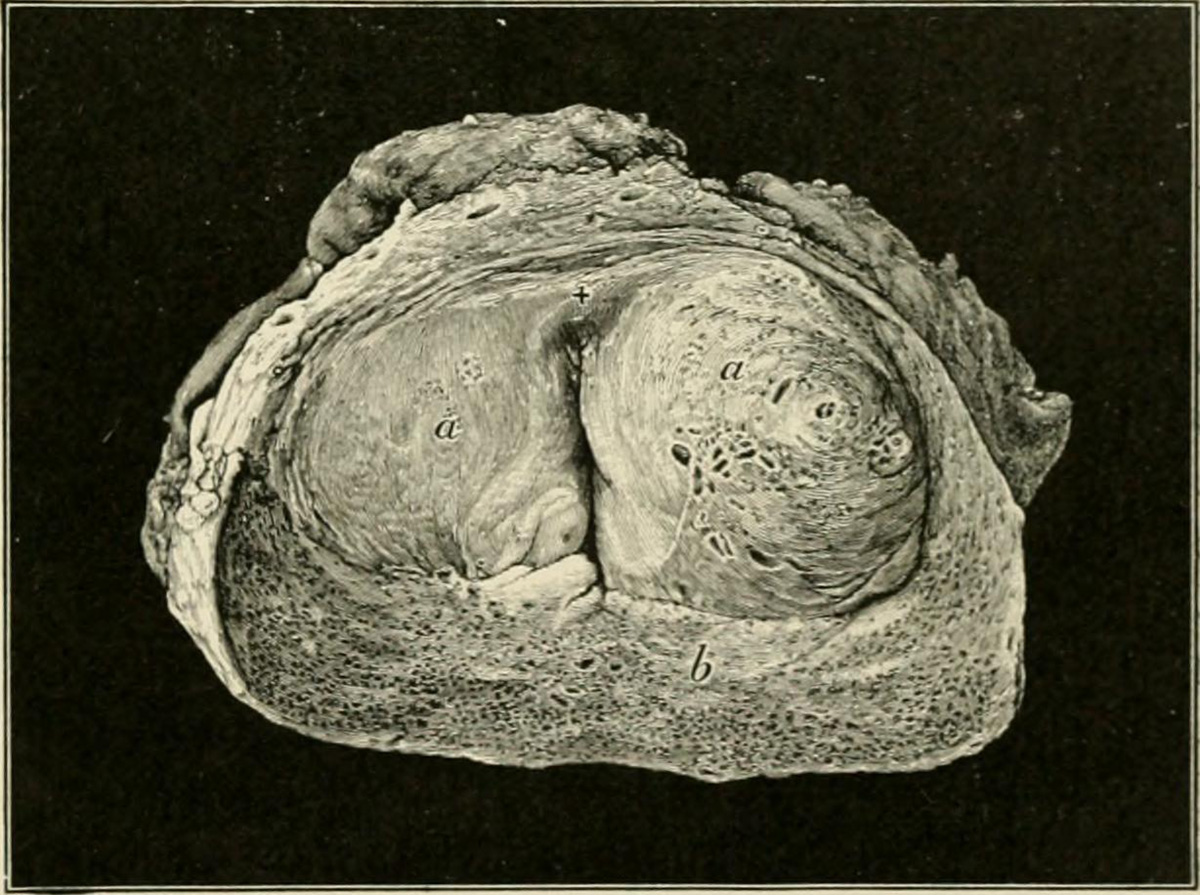
The prostate
Symptoms
Men with prostate cancer, usually have no symptoms, especially at the initial stage of the disease. This is because prostate cancer often occurs in the peripheral areas of the prostate and starts to exert pressure on the urethra and impede urination later on.The most common symptoms of progressing disease that force patients to visit the physician are: frequent urination, difficult urinating, intermittent urination, blood in the urine and semen, pain or burning when urinating, problems with erection, painful ejaculation, frequent pain or stiffness in lower back, weight loss, loss of appetite and weakness in a later stage of the disease.
Treatment
Correct choice of prostate cancer treatment requires considering several factors such as the degree of cancer differentiation, stage of the disease, whether the disease is localized or has nearby or distant metastases, and the age of the patient and symptoms that he/she feels. After consideration of all these, urologist in consultation with oncologists and specialists in nuclear medicine, applys the appropriate treatment. Different therapy methods include surgery, radiation therapy (radiotherapy, radiation), hormonal therapy and sometimes combination of anti-androgen hormones and cytostatics. These procedures can be used alone or in combination.Surgical Treatment
Prostate surgery is applied in the earlier stages of prostate cancer. There are several types of prostate surgery and they may be in the form of partial or complete removal of the prostate.Radical perineal prostatectomy is surgery which is performed under general anesthesia. The incision is located between the scrotum (testicles) and anus. This procedure is minimally invasive and especially applied in obese patients. The regional (nearby) lymph nodes can't be removed by this procedure. Radical retropubic prostatectomy is the surgical procedure which is performed under general anesthesia. The incision is made on the abdominal wall, 2.5 cm above the penis, and the surgery removes the entire prostate gland together with nearby lymph nodes - semen cavities around the prostate. This procedure is the easiest way to preserve the surrounding peripheral nerves that control urination and erection.
Laparoscopic prostatectomy and robot-assisted laparoscopic radical prostatectomy (RALRP) are surgeries which are performed under general anesthesia with a few small incisions in the abdominal wall. Laparoscope is introduced into the abdominal cavity through a small incision by which an urologist surgically removes prostate. In the classic laparoscopy, urologist performs surgery with the help of instruments, while robotic laparoscopy is performed by a device that is connected to the laparoscope, which is managed by an urologist. Transurethral resection of prostate (TURP) is surgery which performs under local anesthesia by introducing cystoscope through the urethra with the help of surgical instruments. By this, the tumor tissue removes if it is available for this kind of surgery. This surgical procedure removes only the tumor, not the entire prostate. Chryosurgery removes the prostate tumor tissue by freezing. This procedure assumes the introduction of the probe into the perineal region (the area between the scrotum and rectum). Rectal microwave probe freezes the prostate and thus destroys the cancer cells in the prostate. This method often damages the tissue around the prostate (bladder), the rectum and the muscles that control urination. Recovery time from the surgery depends on the method of surgical treatment, the patient's age, other associated diseases, obesity and so on.













Your thoughts on this
Loading...