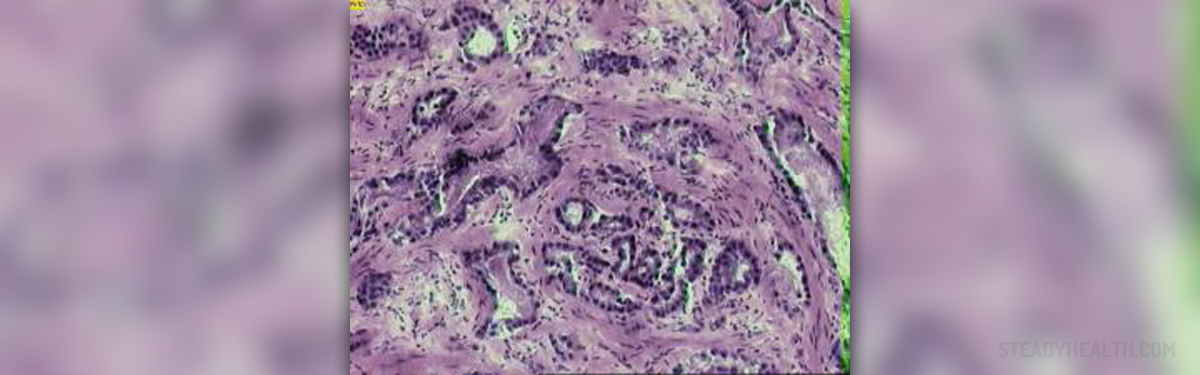
The prostate is a male gland located in the pelvis, to be more precise it lies at the neck of the bladder and in front of the rectum. The gland surrounds the urethra, a tube in charge with transfer of sperm and urine. The most common problem related to the prostate is certainly benign prostatic hypertrophy which affects older men. Apart from that the gland may also be inflamed and then we are taking about prostatitis. However, in certain number of patients there is even a chance of developing prostate tumors, both benign and malign. In case of malign tumors there is a great chance of destruction of the surrounding tissues and spread of the tumor to bones and distant organs. This cancer originates from the secretory glands in the prostate and it is pathohistologically classified as adenocarcinoma.
Causes of Prostate Cancer
The exact cause of prostate cancer has not been identified yet but there are theories about environmental, hormonal, genetic and dietary factors which may be possible contributors to the disease. There is a strong connection between prostate cancer and the age of patients. Namely, the older the man is the odds of getting prostate cancer drastically increase. Furthermore, in the United State African Americans are more likely to develop this type of cancer comparing to white men. And Asian Americans are at lower risk comparing to both, white and African American. People who have had a history of prostate cancer in their families are definitely at higher risk of getting the disease themselves. This particularly refers to those whose first-degree relative (a father or a brother) has had a prostate cancer. There is also a connection between sexually transmitted infections and prostate cancer. And finally, a diet rich in fat as well as exposure to certain chemical agents such as cadmium may be the cause of prostate cancer.
Treatment for Prostate Cancer
There are several treatment modalities for people suffering from prostate cancer. Which of them is going to be applied basically depends on the pathological type of tumor and its grade, the level of PSA, spread to the regional lymphatics, patient's age and general health etc.
Surgery for prostate cancer includes radical prostatectomy and it is only performed in case tumor is limited to the prostate and has not invaded the capsule of the gland or spread to regional lymph nodes. One more surgical option is transurethral resection of the prostate (TURP). In this surgical procedure only part of the prostate is resected. It is indicated in patients suffering from blockage of the urine flow.
Radiation therapy (both external beam radiation therapy and brachytherapy) is another treatment modality. It treats the prostate cancer which has not spread outside the prostate.
And finally, hormonal therapy includes administration of luteinizing hormone- releasing hormone agonists (LHRH) and is prescribed to patients in whom the cancer has spread to distant regions. These patients may also benefit from orchiectomy (surgical removal of both testicles) since these glands may hormonally stimulate the growth of the tumor. Patients may be also prescribed anti-androgens which stop testosterone from working. They include flutamide and bicalutamide.













Your thoughts on this
Loading...