An umbilical hernia, or more commonly known as a belly button hernia, is something that is quite common for both infants and people who are significantly overweight. Often it is caused by putting too much pressure on the abdomen.
Hernia Overview
A hernia is an abnormal growth of a certain part of the body through a tear that has been created in the body in order to open up in a nearby organ.
Usually it is the abdomen that is affected by hernias. The kind of hernia that occurs is defined by what part of the body is in question. When someone has a belly button hernia, there is a bulge on the stomach region that was created by the intestines pushing through the membrane of the person’s abdomen.
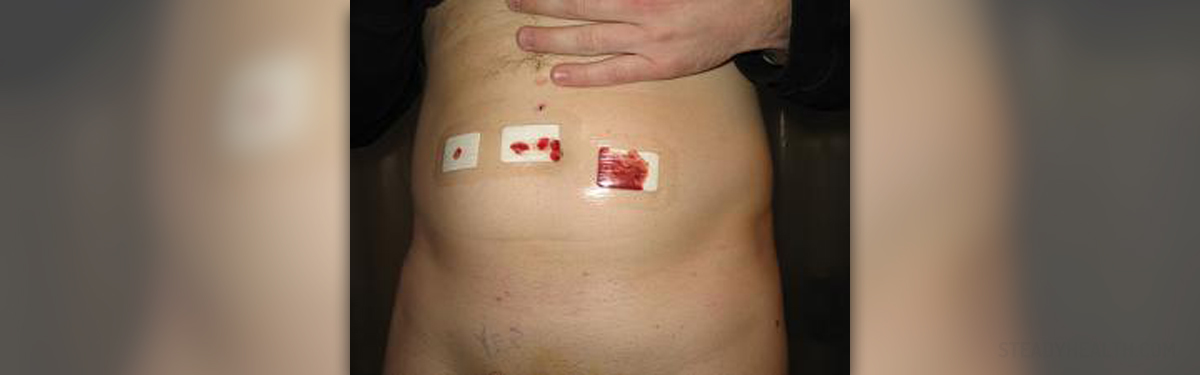
Even though it is a condition that is most common in infants, it can occur in adult men and women as well.
Hernia Causes
The main cause of such a condition is usually from the fact that the person’s stomach muscles are not as strong as they should be.
Since the muscles are weak, they easily allow the abdominal tissues to move right through them. The greatest risk of developing a belly button hernia occurs in children that are younger than six months.
Hernia Treatment and Risks Factors
Sometimes the hernia will go away on its own as the child grows older and its muscles develop. It can go away within a year or it may take two or three. However, if the hernia does not recede within five years, a surgery will be needed to get rid of it.
There are many things that can lead to an adult developing a belly button hernia, including too much stress, not enough sleep, and lack of a balanced diet and the absence of a proper exercise program.
If the hernia appears, it will probably appear in the form of a lump behind the naval, and it will be accompanied with slight pain and discomfort.
Hernia Surgery
Since this kind of hernia is fairly common, there are surgical measures that have been developed to get rid of it.
Surgery is also the only real option for getting rid of the hernia, since there is no medication or other treatment that can repair the problem.
The surgical procedure is fairly simple and it involves a simple removal of the hernia and then a stitching of the affected area. The patient will receive a general anesthetic and sleep through the process.
The recovery time is also very minimal and the patient should be able to return to his or her normal life in a matter of days.
- There are four possible locations for mesh placement in umbilical hernia repair: preaponeurotic (onlay technique), on the fascial layer (fixed to the ring), in the retromuscular space (sublay technique) or on the preperitoneal space. In our study we analyzed the long-term follow-up results of the three most popular umbilical hernia operating techniques (Keel, open mesh repair and laparoscopic).
- One hundred and forty-six patients were operated on using suture repair, 52 using open mesh and 18 using laparoscopic repair technique. 77.8% of patients underwent long-term follow-up.
- The postoperative wound complication rate and long-term postoperative complaints were significantly higher in the open mesh repair group. The overall hernia recurrence rate was 13.1%.
- Only 2 (1.7%) patients with small hernias ( 30 kg/m2, diabetes and wound infection were independent risk factors for umbilical hernia recurrence.
- The overall postoperative complication rate was 12% in the early follow-up period. This rate was higher in the open mesh repair group than in the laparoscopic and suture repair groups (26.9% vs. 11% vs. 6.8%; p > 0.05). Most of the complications occurred in patients with hernia defect size > 4 cm, but with no significant difference.












Your thoughts on this
Loading...