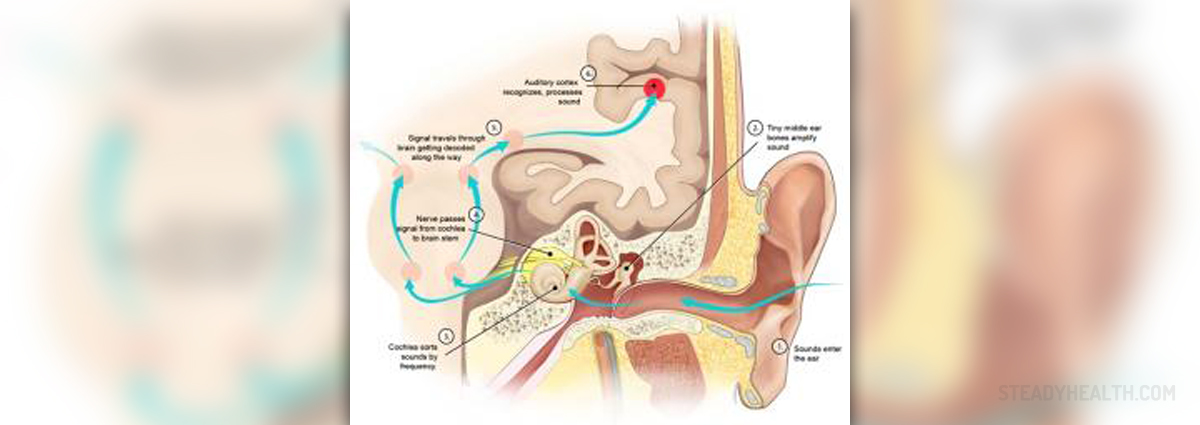
Sudden hearing loss is considered a serious medical condition. Hearing loss can be classified as sudden only if it occurs within 72 hours or less (usually over few hours) and in case hearing reduction is greater than 30 dB over at least 3 contiguous frequencies. The condition generally affects people between 30 and 60 years of age and is equally present in both genders.
In majority of cases sudden hearing loss affects only one ear but it may be possible that a person develops bilateral sudden hearing loss. Apart from hearing problems there may be additional symptoms such as vertigo, tinnitus etc. The condition is either short-lived or in severe cases the person develops permanent hearing loss.
Sudden Hearing Loss - Causes
Many experts are simply unable to identify the underlying cause of sudden hearing loss, hence the condition is most commonly classified as idiopathic. However, it seems that viruses represent the cause of sudden hearing loss in approximately 60% of all cases. Many viruses can be blamed for this condition and influenza type B, mumps, rubeola, varicella-zoster, measles and infectious mononucleosis are only some of them.
Diagnosing Sudden Hearing Loss
Patients notice they have hearing problems and they turn to their doctors. So, in most cases there is a recent decline in hearing. A well experienced doctor first performs ORL exam. What follows is audiometry. This is a testing for hearing ability able to determine a subject's hearing levels and can effectively record hearing loss.
Differential diagnosis includes several more illnesses such as viral disease, Lyme disease, vascular disease, autoimmune phenomena, parilymph fistulae, acoustic neuroma and Meniere's disease. It is essential to exclude all other conditions prior to setting a definitive diagnosis of sudden hearing loss.
Sudden Hearing Loss - Treatment
Treatment for sudden hearing loss usually includes administration of steroids (most commonly Prednisone). There have been many studies regarding treatment of hearing loss and treatment success data vary a lot. For example, some patients have responded well when they were administered transtympanic steroids since they have been unable to tolerate oral form of the medication.
Another treatment option is hyperbaric oxygen therapy. This particular treatment includes 90-minute sessions of breathing pure oxygen at 2.2 atmospheric pressure in a multiperson chamber. Patients require 10 of such sessions in order to regain hearing loss.
There is not much evidence regarding treatment with Carbogen and MgSO4 but these treatments may be adopted in the near future.
And finally, since the condition may be caused by viral infection it is logical for doctors to opt for available antiviral drugs.













Your thoughts on this
Loading...