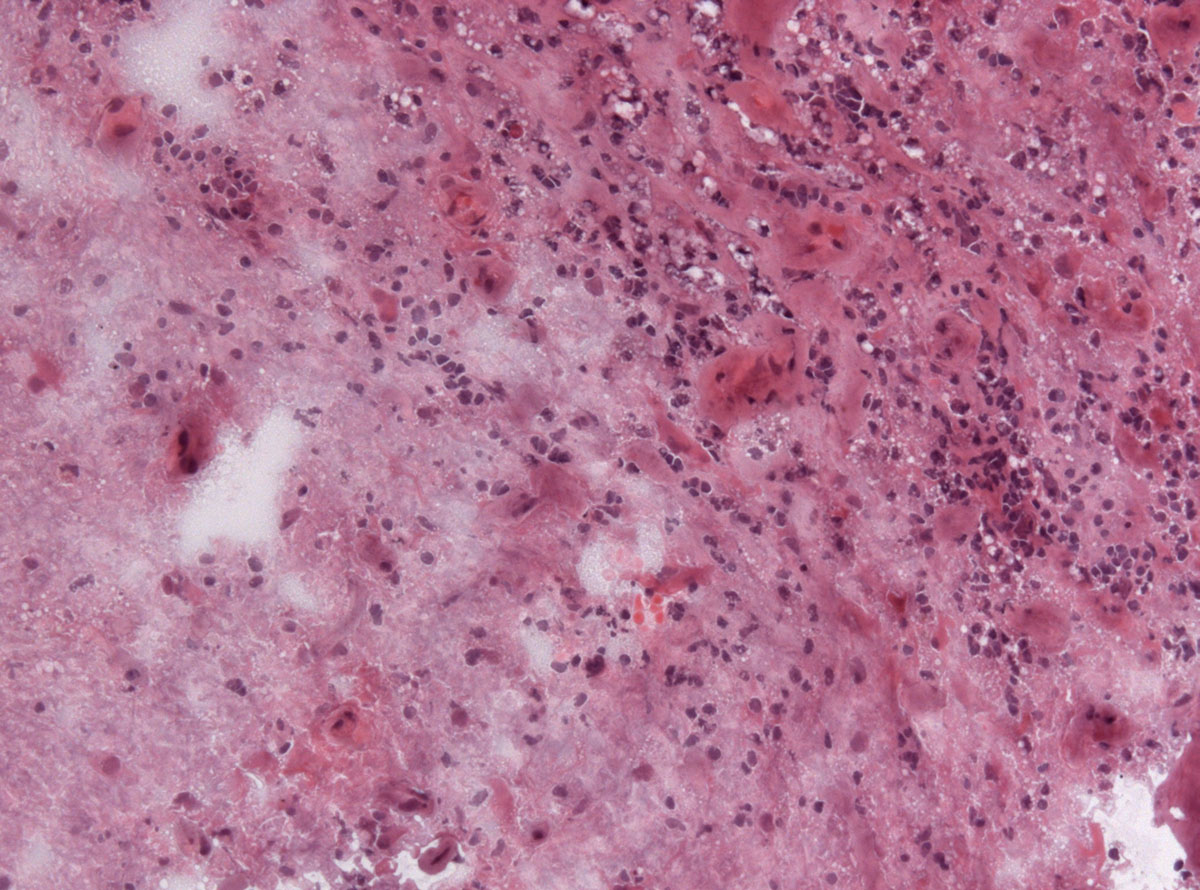
Introduction to Encephalitis
Encephalitis is a medical term for inflammation of the brain. In majority of cases encephalitis develops due to viral infection. The condition almost never occurs in severe form. Many experts believe that apart from reported and confirmed cases of encephalitis there are many cases which stay unrecognized due to mild symptoms and signs of inflammation.
Encephalitis can be classified as primary or secondary. Primary encephalitis develops as a consequence of direct viral infection of the brain and spinal cord while secondary form of the disease first affects other parts of the body and then spreads to the brain.
Encephalitis Causes
Some examples of viral encephalitis are encephalitis caused by Herpes viruses, encephalitis caused by Abroviruses (transmitted by mosquitoes, ticks and other insects) and encephalitis caused by Rabies.
Not all herpes viruses are capable to cause encephalitis. Only HSV type 1 which causes cold sores may also cause fatal sporadic encephalitis. Fortunately, this condition is very rare. Furthermore, Varicella-zoster virus is another member of Herpes viruses able to induce encephalitis. Varricela-zoster encephalitis is mild in nature. And finally, encephalitis can occur due to one more member of Herpes virus family. This is encephalitis caused by Epstein-Barr virus. Encephalitis caused by Epstein-Barr virus can in small percentage be fatal.
Even though encephalitis in majority of cases occurs due to viral infection the condition may occur due to bacterial and parasitic infection as well. One example of bacterial encephalitis is Lyme encephalitis. In Lyme disease encephalitis develops in later stage of the disease and leads to permanent damage to the affected part of the brain. Some examples of parasitic encephalitis include encephalitis caused by toxoplasmosis. This type of encephalitis generally affects immunocompromised patients.
Several more causes of encephalitis include encephalitis associated with childhood infections, encephalitis associated with overreaction of the immune system and several mosquito -borne encephalitis.
In some children encephalitis develops after they have been vaccinated against certain infective illnesses. This side effect is possible after vaccination against measles, mumps or rubella.
Some viruses transmitted via insects (mosquitoes, ticks etc.) are able to cause encephalitis epidemics. The organisms which transfer the virus to humans are known as vectors. Eastern equine encephalitis normally affects horses and birds. However, this type of encephalitis can also affect humans. Fortunately, the incidence of Eastern equine encephalitis in humans is very low. The condition can be mild and fatal cases affect only one-third of all patients. Symptoms of the infection fully develop 10 days after the bite of an infected mosquito. Western equine encephalitis affects horses and birds and sometimes humans. This encephalitis is more severe than Eastern equine encephalitis particularly if it affects infants. St. Louis encephalitis is also transmitted from birds to humans while La Crosse encephalitis primary affect chipmunks and squirrels. And finally, there is a West Nile encephalitis. This type of encephalitis is spread from birds to humans. In case of West Nile encephalitis there is even a chance of spread of the infection from one person to another. Fortunately, this type of encephalitis is mild in nature and severe form of the disease only occurs in older adults and immunocompromised patients.
















Your thoughts on this
Loading...