
Introduction
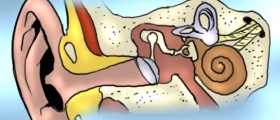
Sudden hearing loss can be defined by various factors suchas frequency spectrum of the loss, audiometric criteria, time course andseverity. Sudden hearing loss is the term used for both rapidly progressive andabrupt losses. It may also be used in all instances of distorted speechperceptions, selective frequency losses and several other similar medicalconditions. The diagnosis of sudden hearing loss involves the use of a commoncriterion which is a sensorineural hearing loss greater than 30 decibels whichspreads over 3 contiguous pure tone frequency within the period of only threedays. In most cases it is possible to recover the hearing to a certain degree.There are four different theoretical pathways of the postulated pathophysiologyfor idiopathic sudden sensory hearing loss and those include labyrinthine viralinfections, labyrinthine vascular compromises, intracochlear membrane rupturesand immune-mediated inner ear diseases. Sudden hearing loss may be a symptom ofany of these theoretical possibilities.
Four Possibilities
One of the causes of sudden idiopathic sensory hearing lossis viral infection. In some cases there is evidence of viral seroconversion orinner ear histopathology with viral infections of the ear. Not all patientssuffer from viral illnesses, as they only tend to affect up to one third ofthem. It is not yet fully proven that viral infections can be implicated as acause sudden idiopathic sensory hearing loss. Cochlea is an organ which doesnot have any collateral vasculature, when it comes to speaking of its bloodsupply. Its functioning changes pretty much when the blood supply suffers anychanges. Cochlea may suffer from vascular compromise due to vasospasm, reducedblood flow, embolus and thrombosis, and they all may lead to the occurrence ofsudden idiopathic sensory hearing loss. The alterations in cochlear blood floware usually triggered by reduced supplies of oxygen. Another possible cause ofsudden idiopathic sensory hearing loss is intracochlear membrane rupture. Thereare membranes which separate the middle and the inner ear, and there are alsomembranes inside the cochlea which separate the endolymphatic and perilymphaticspaces. In theory, a rupture of any of the aforementioned membranes could beheld responsible for the onset of sudden idiopathic sensory hearing loss. Thelast of the four different possibilities is called immune mediated inner eardisease. It is a concept introduced in 1979 and is often associated also withthe progressive sensorineural hearing loss. This medical condition affects both sexes and all age groups.














Your thoughts on this
Loading...