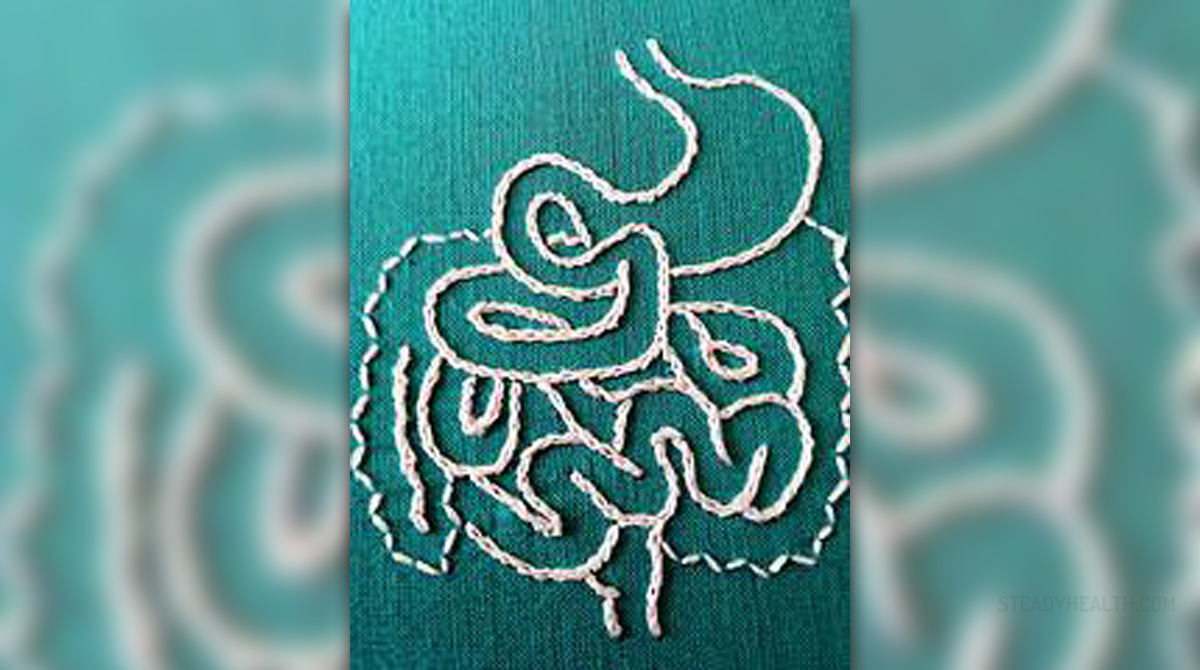

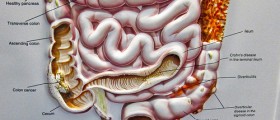
Sigmoidoscopy is a certain type of medical examination which allows the doctor to look inside the lower part of the bowel. The procedure itself is not associated with any painful sensations, but the patient may sometimes experience slight discomfort after the procedure. The discomfort is usually triggered by the small amount of air blown by the doctor into the intestine so that he or she can see inside it much more clearly. There are two main different types of sigmoidoscopy and those are flexible sigmoidoscopy and rigid sigmoidoscopy. The flexible type of sigmoidoscopy allows the doctor to look inside the large intestine from the rectum and the last part of the colon which is medicinally referred to as the sigmoid. This is how the procedure actually got its name. This type of procedure is commonly used in cases whrn a person suffers from constipation, abdominal pain or diarrhea. The procedure may also be very efficient in detecting malignant polyps, benign polyps and even early signs of cancer in the rectum or the descending colon. The process of flexible sigmoidoscopy allows the physician to also check for ulcer, abnormal growths, inflammatory conditions and intestinal bleeding in the rectum and the descending colon. Unfortunately it cannot be used for the detection of cancer or polyps in the transverse or the ascending colon. The section of the large intestine which can be examined by utilizing the process of sigmoidoscopy is actually relatively small. The procedure requires the patient to lie on the left side on the examining table before the physician insert a short lit tube which is flexible into the rectum. Once it gets inserted it is slowly and carefully guided on its way to the colon. The tube itself is medicinally referred to as sigmoidoscope. It presents the image of the inside of the colon and the rectum so that the doctor can carefully inspect those parts of the human body. It is also necessary to blow some air through the scope so that the organs can get inflated and provide the physician with much clearer information. If the doctor finds any inflamed tissue, polyps or other unusual things in the colon or the rectum, he or she can remove those by using certain instruments which get inserted through the scope. He or she can also obtain a piece of tissue for further tests in the laboratory. This type of procedure is called biopsy. There are certain complications which may be associated with sigmoidoscopy such as puncture or bleeding of the colon, but those occur only in rare cases. The entire procedure last for 10 to 20 minutes, depending on the individual case and it may sometimes cause the patient to feel a little cramping and pressure in the lower portions of the abdomen. Once the air leaves the colon, these discomforts usually disappear on their own. The second type of sigmoidoscopy is the rigid sigmoidoscopy but it is not used that much anymore since the invention of the aforementioned flexible type of sigmoidoscopy. In some cases of anal or rectal disease such as the inflammatory rectal disease or bleeding per rectum it still may be useful to a certain degree. In order to be performed properly, the patient needs to lie down on the left side during the process of rigid sigmoidoscopy. The bowels need to be emptied prior to the process and the person also needs to undertake a digital rectal examination before rigid sigmoidoscopy. The sigmoidoscope gets lubricated before it is inserted with an obturator in general direction of the navel. Once the direction gets changed the obturator can be removed and allow the physician to penetrate even further by utilizing direct vision. The rectum can be distended by insufflating the air with bellows.
Is the procedure safe?
The procedure is completely safe, even though in some rare cases it may involve punctures and internal bleeding.
Preparation before sigmoidoscopy
One needs to be informed about certain things that need to be done in order to get prepared for the procedure appropriately. On the very day that the examination takes place the suppository or an enema need to be used in order to soften the stool of the patient. The stool needs to be removed from the lower parts of the intestine which are to be examined. So the rectum and the colon need to be completely empty and clean in order for the procedure to be completely safe and thorough. Only clear liquids are allowed for 12 to 24 prior to the examination. Those include diet soft drinks, plain tea, plain coffee, water, strained fruit juice, gelatin, broth and bouillon. The patient needs to receive an enema or a laxative the night before the procedure so that the intestines can get washed out thoroughly. The procedure does not require any sedation, excluding certain cases which exceed the levels of the splenic flexure.











Your thoughts on this
Loading...