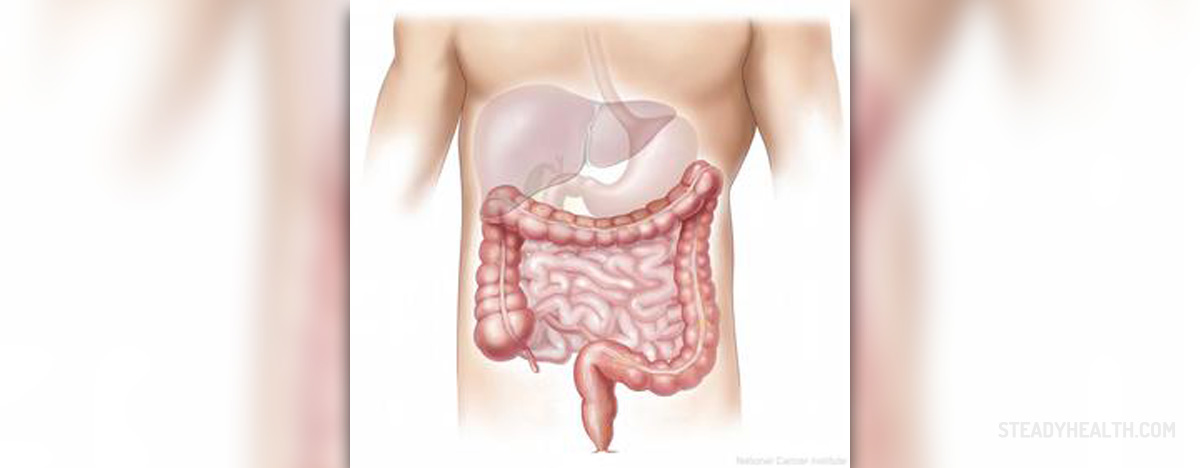
A digestive disorder can be diagnosed on the basis of an accurate medical history and a physical examination. Further extensive diagnostic evaluation can be used to confirm the diagnosis and identify the severity of the problem. All of these help physicians to determine appropriate treatment approach.
Diagnosing Digestive Disorders
Medical History and Physical Examination
Medical history or anamnesis is taken by a physician by asking specific questions related to the symptoms a patient is experiencing. For instance, if the patient suffers from the abdominal pain, the doctor will ask the patient to describe the pain and tells what relieves it or aggravates it.
During the physical examination performed to identify the digestive disorder, the physician will observe body weight and the overall appearance of the patient. However, the physician will particularly focus on the abdomen, anus and rectum.
While examining the abdomen, the doctor will look for distention of the abdominal wall which may indicate abnormal growth or enlargement. The doctor will also palpate the abdomen to note if there is tenderness or organ enlargement. Rebound tenderness, which is the pain caused by pressure on the abdomen, typically signals inflammation or infection of the lining of the abdominal cavity.
To examine the anus and rectum, the doctor uses a gloved finger. The doctor may also take a sample of stool to check for the presence of hidden blood.
Diagnostic Procedures for Digestive Problems
Endoscopy
Endoscopy is a diagnostic procedure used to examine the internal organs with the help of a flexible, thin, lightened tube called endoscope. An endoscope can allow the doctor to look inside the esophagus (esophagoscopy), the stomach (gastroscopy), the first section of the small intestine (upper gastrointestinal endoscopy) and the rectum (anoscopy). Endoscopic procedure to view the lower segment of the large intestine, rectum and anus is called sigmoidoscopy and the procedure to examine the entire length of the large intestine, rectum and anus is called colonoscopy.
Endoscopy can be also used to obtain a tissue sample (endoscopic biopsy). The sample is then taken to laboratory to be tested for inflammation, infection or cancer. Finally, endoscopy can be used for treatment of digestive disorders. It can stop the bleeding, remove a growth or destroy abnormal tissue.
Capsule Endoscopy
This procedure uses a pill camera to view the inner lining of the intestine. The patient swallows the capsule which then sends images to a receiver that is attached to the patient’s belt or worn in a cloth pouch.
LaparoscopyLaparoscopy is another diagnostic procedure used to examine the abdominal cavity with the help of the endoscope. It is done by making a small incision in the abdomen used for insertion of an endoscope. Laparoscopy can be used for diagnosing, taking biopsies and performing a surgical treatment. The procedure is done under general anesthesia.
X-ray Imaging
X-ray imaging test is often used to diagnose a digestive disorder. It can reveal a blockage or paralysis of the digestive tract, abnormal air patterns in the abdominal cavity and enlargement of the liver, kidneys and spleen.
Liquid barium x-ray is done to observe problems that may not show on standard x-ray test. This procedure allows the doctor to see out the contours and lining of the esophagus, stomach and small intestine when the patient swallows a meal containing barium.













Your thoughts on this
Loading...