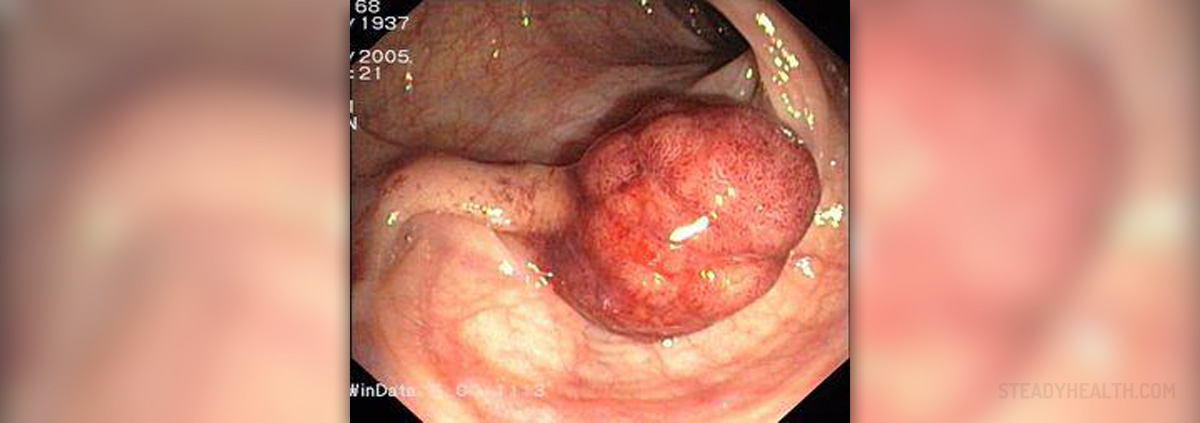
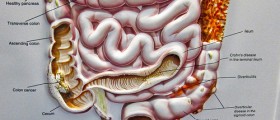
A polyp in the colon is a growth found on the lining of the colon also known as large bowel. Colon polyps can be flat or raised and range in size from 2 mm to 5 cm or more in diameter. Colon polyps are generally benign but may become cancerous. Types of cells that form the polyps determine which polyp will turn into a cancer.
Types of Polyps
Common type of a polyp in the colon is a metaplastic also known as hyperplastic polyp. Metaplastic polyps are typically small growths that have low risk of becoming malignant.
However, the most common type of a polyp is adenomatous polyp or adenoma which has a potential of becoming cancer. Risk for adenomatous polyp increases with age and about 50% of people over the age of 60 have at least one adenomatous polyp. The larger this type of polyp grows the higher is risk for the polyp to develop into cancer.
Familial polyposis coli also known as familial adenomatous polyposis (FAP) is an inherited condition characterized by formation of hundreds of adenomatous polyps in the colon. This disorder most often evolves into colon cancer.
Juvenile polyps are rare type of colonic polyps that affect older children and adolescents. This condition often involves a single polyp with a low risk of developing into cancer.
Peutz-Jeghers polyps, associated with Peutz-Jeghers syndrome, are usually found in young adults. Apart from the colon, these polyps can also develop in the small intestine. This type of polyps carries a slight risk of malignancy.
Inflammatory pseudopolyps usually affect individuals with Crohn’s disease or ulcerative colitis. They are benign sort of polyps.
Cronkhite-Canada syndrome is a very rare condition associated with malabsorption. This disorder is usually found in middle-aged and older adults and causes hyperpigmentation, nail atrophy and multiple colon polyps.
Causes of Colon Polyps
Colon polyps develop due to genetic mutations in the colon lining cells. Colon polyps often run in families. Lifestyle risk factors include high intake of fatty foods, smoking, alcohol drinking and obesity. Aging also plays role in development of polyps in the colon and people aged 50 years or older have increased risk of the condition.
Symptoms of Colon Polyps
Colon polyps are usually asymptomatic. However, when they reach 2cm or more in diameter symptoms may occur. Symptoms of polyps in the colon include changes in bowel habits, blood in the stool and rectal bleeding.
Diagnosis of Colon Polyps
Colon polyps can be detected using a screening examination called colonoscopy. During colonoscopy long flexible tube with a camera is inserted through the anus to examine the entire length of the large intestine. Barium enema is also used to identify asymptomatic polyps. Barium enema examination involves pouring barium liquid into the rectum before taking x-rays of the colon. Sigmoidoscopy can also help to detect colon polyps. This procedure is similar to colonoscopy but is used to examine only the lowest part of the large intestine.
Treatment for Colon Polyps
Colon polyps can be removed during colonoscopy. The procedure is called polypectomy. The polyps can be also removed surgically.
- medlineplus.gov/ency/article/000266.htm
- www.nhs.uk/conditions/bowel-polyps/
- Photo courtesy of J. Guntau by Wikimedia Commons: commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:Polyp.jpg










Your thoughts on this
Loading...